Fig. 1
Image
Figure Caption
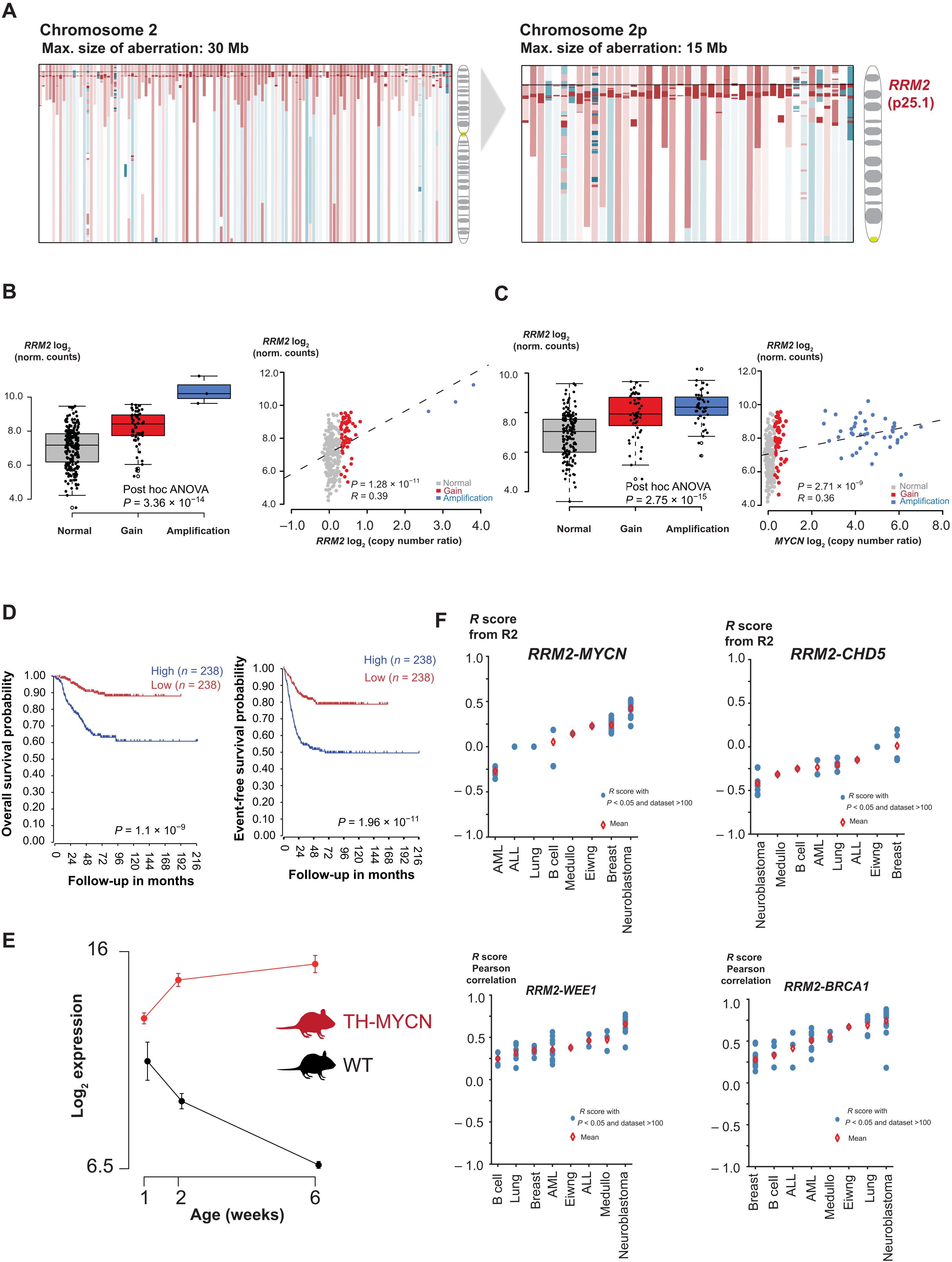
Fig. 1. In silico analysis of genomic and transcriptomic data of primary neuroblastoma converges toward RRM2 as a top-ranked 2p codriver in high-risk neuroblastoma.
(A) Array CGH (comparative genomic hybridization) profiles of >200 high-risk neuroblastoma cases converge toward the RRM2 gene (2p25.1) as recurrently gained on 2p (red: gained/amplified region and blue: deleted region). (B) Left: Boxplot indicating the gene dosage effect for RRM2 expression in relation to the RRM2 copy number status. Right: Correlation analysis of RRM2 expression with RRM2 copy number data [National Research Council (NRC) neuroblastoma cohort (n = 283); hgserver2.amc.nl]. ANOVA, analysis of variance. (C) Left: Boxplot indicating the gene dosage effect for RRM2 expression in relation to the MYCN copy number status. Right: Correlation analysis of RRM2 expression with MYCN copy number data [NRC neuroblastoma cohort (n = 283); hgserver2.amc.nl]. (D) High RRM2 expression levels correlate to a poor overall and event-free neuroblastoma patient survival [Kocak cohort (n = 283); hgserver2.amc.nl]. (E) Rrm2 expression is strongly up-regulated during TH-MYCN–driven neuroblastoma tumor development. (F) Pearson correlation of RRM2 and its upstream regulators (MYCN, WEE1, BRCA1, and CHD5) in expression data from various cancer entities available (hgserver2.amc.nl). AML, acute myeloid leukemia; ALL, acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Sci Adv