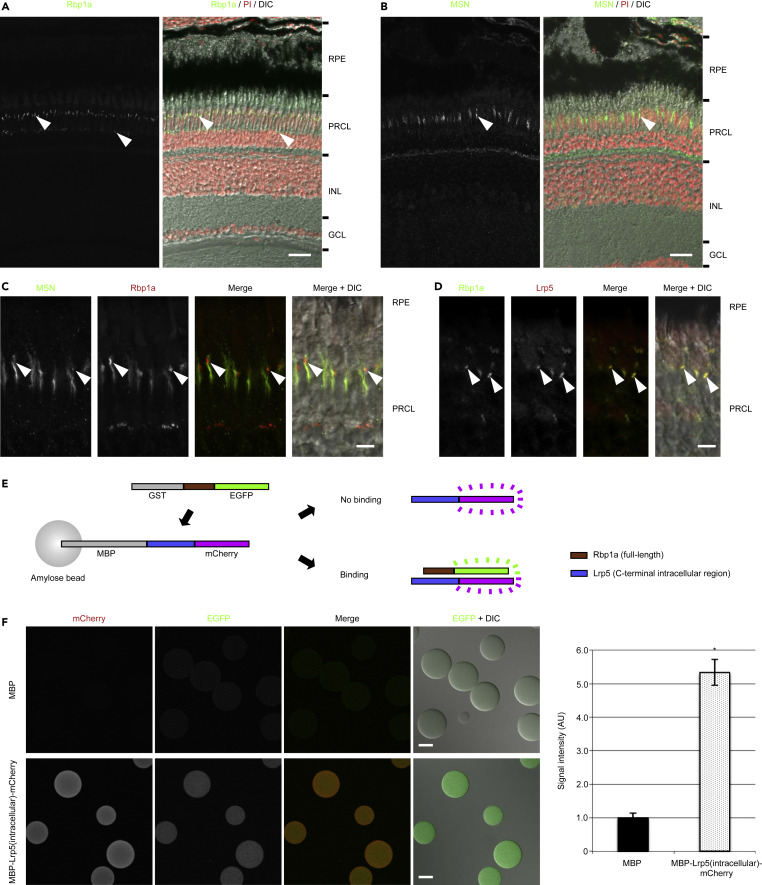
Fig. 4 Figure 4. Lrp5 and Rbp1a Proteins Are Colocalized in the Outer Retinas and Bind Directly In Vitro. (A) Staining of Rbp1a protein was observed in the outer retina (arrowheads). Nuclei were stained with propidium iodide (PI) (red). (B and C) Rbp1a signal overlapped well with MOESIN (MSN), a marker of the microvilli of the RPE, and strong signal was observed at the tip (arrowheads), which suggested that Rbp1a was concentrated in the tip of the microvilli in the RPE. (D) Staining of Lrp5 protein with Rbp1a protein revealed that Lrp5 was colocalized with Rbp1a at the concentrated region (tip) of the microvilli of the RPE (arrowheads). (E) Experimental design of binding assay. Binding is detected by fluorescence from EGFP. (F) EGFP signal was observed on the beads in which the intracellular region of Lrp5 protein was fused to MBP (lower panels), whereas it was not detected on the beads in which MBP alone was present (upper panels) (MBP, 1.0 ± 0.1 for 8 beads; MBP-Lrp5(intracellular)-mCherry, 5.3 ± 0.4 for 6 beads). Data are represented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.0000005. DIC, differential interference contrast; GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; PRCL, photoreceptor cell layer; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium. Scale bars, 20 μm in (A) and (B), 5 μm in (C) and (D), and 50 μm in (F).
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ iScience