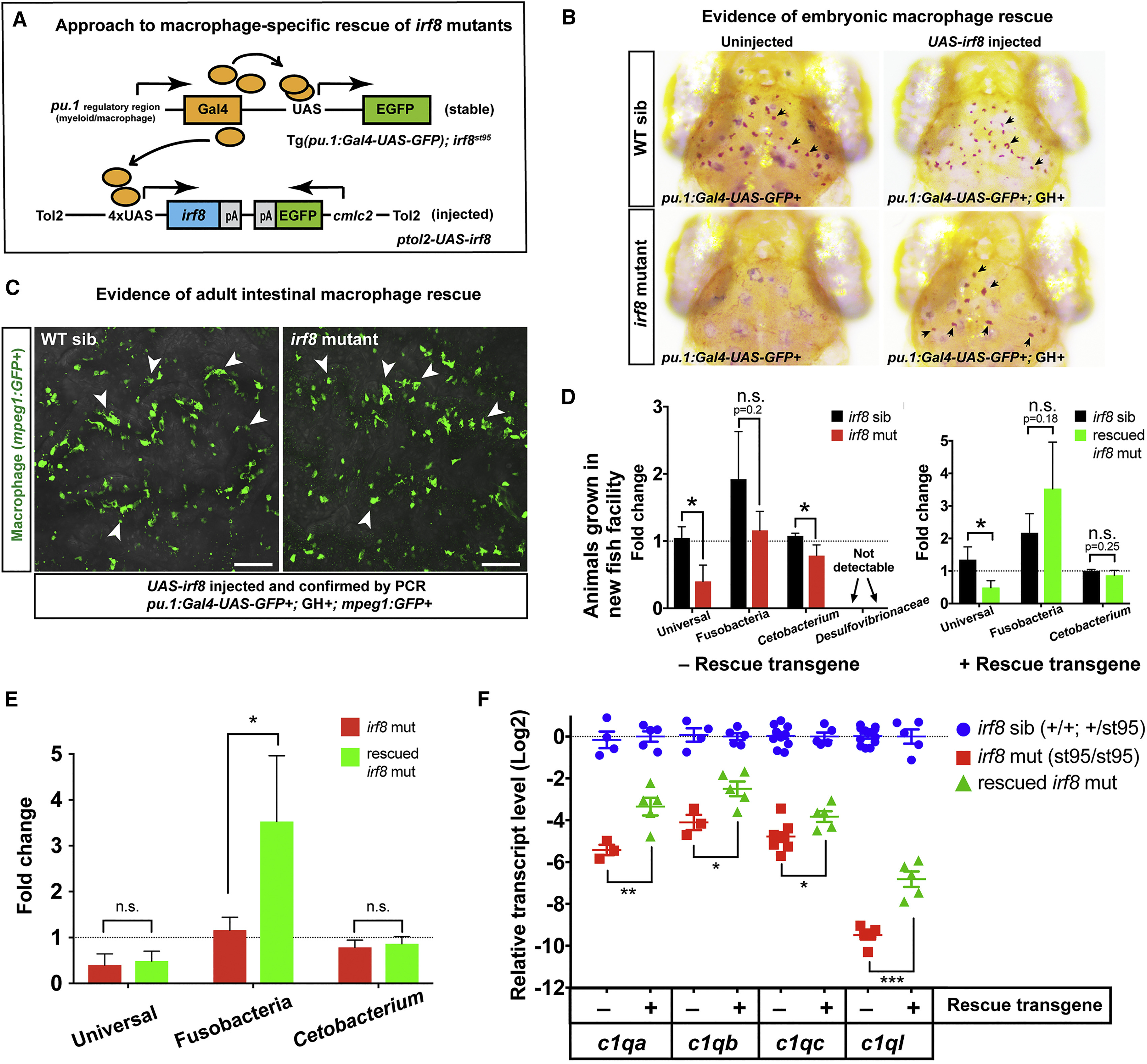
Fig. 6
Mosaic Rescue of Macrophages in irf8−/− Mutants Is Sufficient to Restore Commensal Microbiota and Complement c1q Expressions
(A) Schematic illustrating the genetic constructs used to generate rescue of macrophages in irf8 mutants.
(B) In contrast to the negative controls (uninjected irf8 mutants), which have no brain macrophages, several brain macrophages (arrows) are recovered in the pu.1:Gal4-UAS-GFP+/UAS-irf8-injected embryos.
(C) pu.1:Gal4-UAS-GFP+/UAS-irf8-injected embryos were raised to adulthood and were found to exhibit recovery of intestinal macrophages (arrows) in the irf8 mutant adult guts. Images show gut segment S7 visualized from the lumen side.
(D) Relative abundance of gut microbes in the adult intestine was assayed by qPCR in irf8 mutants and their siblings with the rescue construct and at baseline without the rescue construct.
(E) Comparison of relative bacterial levels between irf8 mutants and macrophage-rescued irf8 mutants.
(F) Fold difference in target c1q genes. Irf8 mutants with the rescue construct were compared to baseline irf8 mutants (control data are represented from Figure 5A). Each symbol represents an individual animal.
Scale bars show 50 μm. Statistical significance was determined by a Student’s t test. 3 or more animals per group were analyzed for all experiments. Error bars show SEM. GH, cmlc2:GFP expression (GFP+ heart). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. mut, mutant; sib, heterozygous or WT sibling; WT, wild-type. See also Figures S6 and S7 and Table S3.