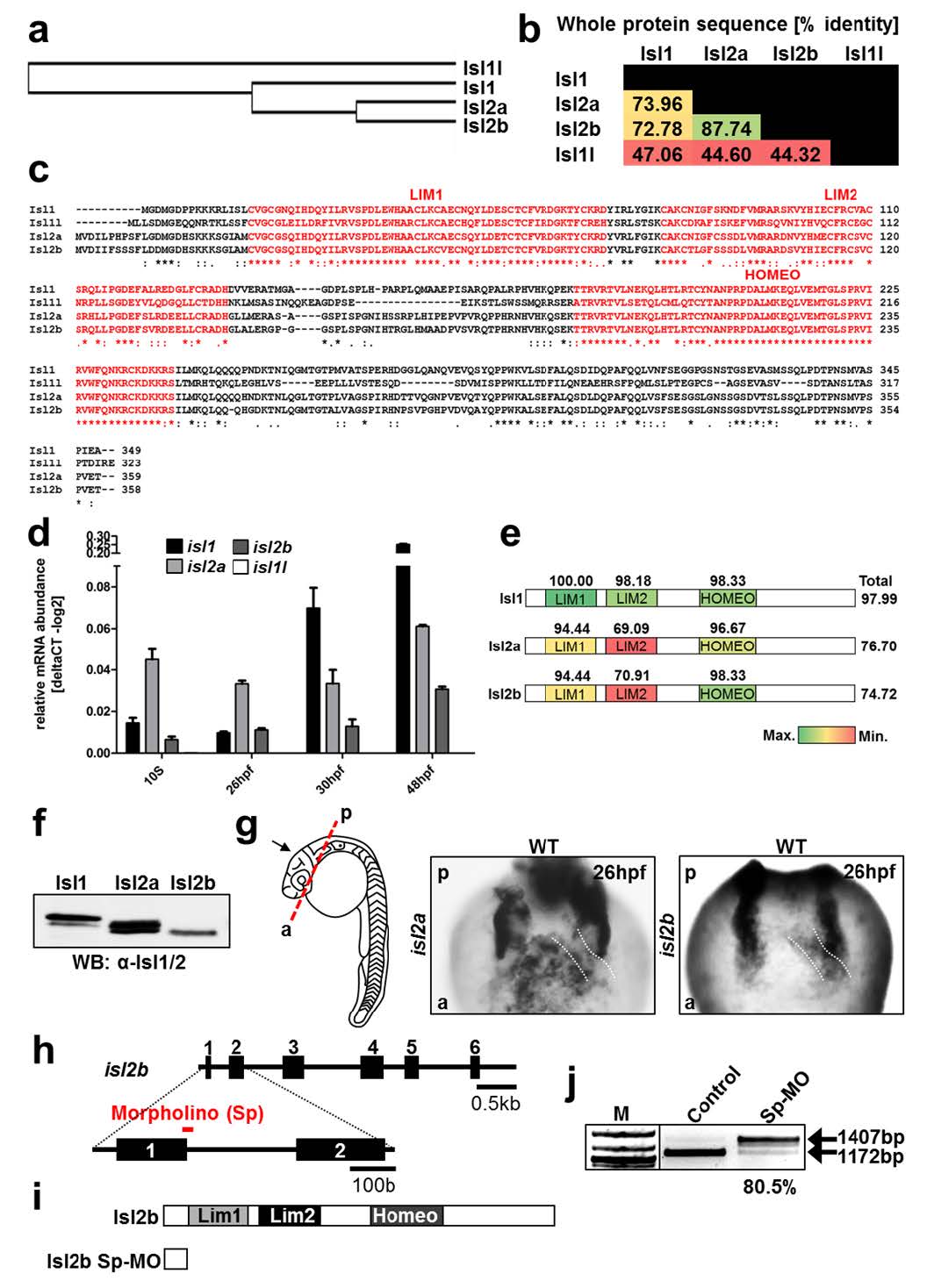
Fig. S1
Conservation and expression of Islet family members.
(a) Guide tree of Isl1, Isl1l, Isl2a and Isl2b protein alignment (D. rerio) generated using the Protein Knowledgebase (UniProtKB). (b) Amino acid sequence alignment of Isl1, Isl1l, Isl2a and Isl2b (D. rerio) performed with Blastp (NCBI). Values represent % of identical amino acids. Red color indicates a lower percentage and green color a higher percentage of identity. (c) Amino acid sequence alignment of Isl1, Isl1l, Isl2a and Isl2b (D. rerio) performed using the Protein Knowledgebase (UniProtKB). The LIM1, LIM2 domains and the homeodomain (HOMEO) are highlighted in red. Asterisks (*) indicate positions with a single, fully conserved residue. Colons (:) indicate conservation of amino acids with highly similar properties and periods (.) with weakly similar properties. (d) Relative mRNA expression of isl1, isl1l, isl2a and isl2b at 10 s, 26 hpf, 30 hpf and 48 hpf. (e) Schematic representation of Isl1, Isl2a and Isl2b (D. rerio). The functional domains, as well as the entire amino acid sequences were aligned to mouse Isl1, whose protein sequence is identical to that of human Isl1. Numbers represent the percentage of identity of zebrafish Isl1, Isl2a and Isl2b with mouse Isl1. (f) Western blot analysis of total protein extracts from HEK293T cells transiently expressing zebrafish isl1, isl2a and isl2b using an anti-Isl1/2 antibody. (g) In situ hybridization for isl2a and isl2b at 26 hpf. Before in situ hybridization, the head was removed as indicated by the red dashed line and images were taken in the direction of the black arrow. White dashed lines indicate the position of the heart tube. The highly stained bilateral structures represent the pharyngeal arches. (h) Schematic representation of the isl2b genomic locus and the binding sites of the morpholino oligo (shown in red). The loss of proper exon-intron junction recognition leads to an altered mRNA containing a premature stop-codon. (i) Schematic representation of the Isl2b protein and Isl2b-morphant protein (bottom). (j) RTPCR analysis of isl2b-splice morpholino-injected embryos. The efficiency of isl2b Sp-MO was analyzed by PCR using primers spanning the first intron of the isl2b gene. This analysis indicated loss of spliced isl2b mRNA (1172 bp band) in embryos injected with the isl2b Sp-MO.