Fig. 2
Fig. 2
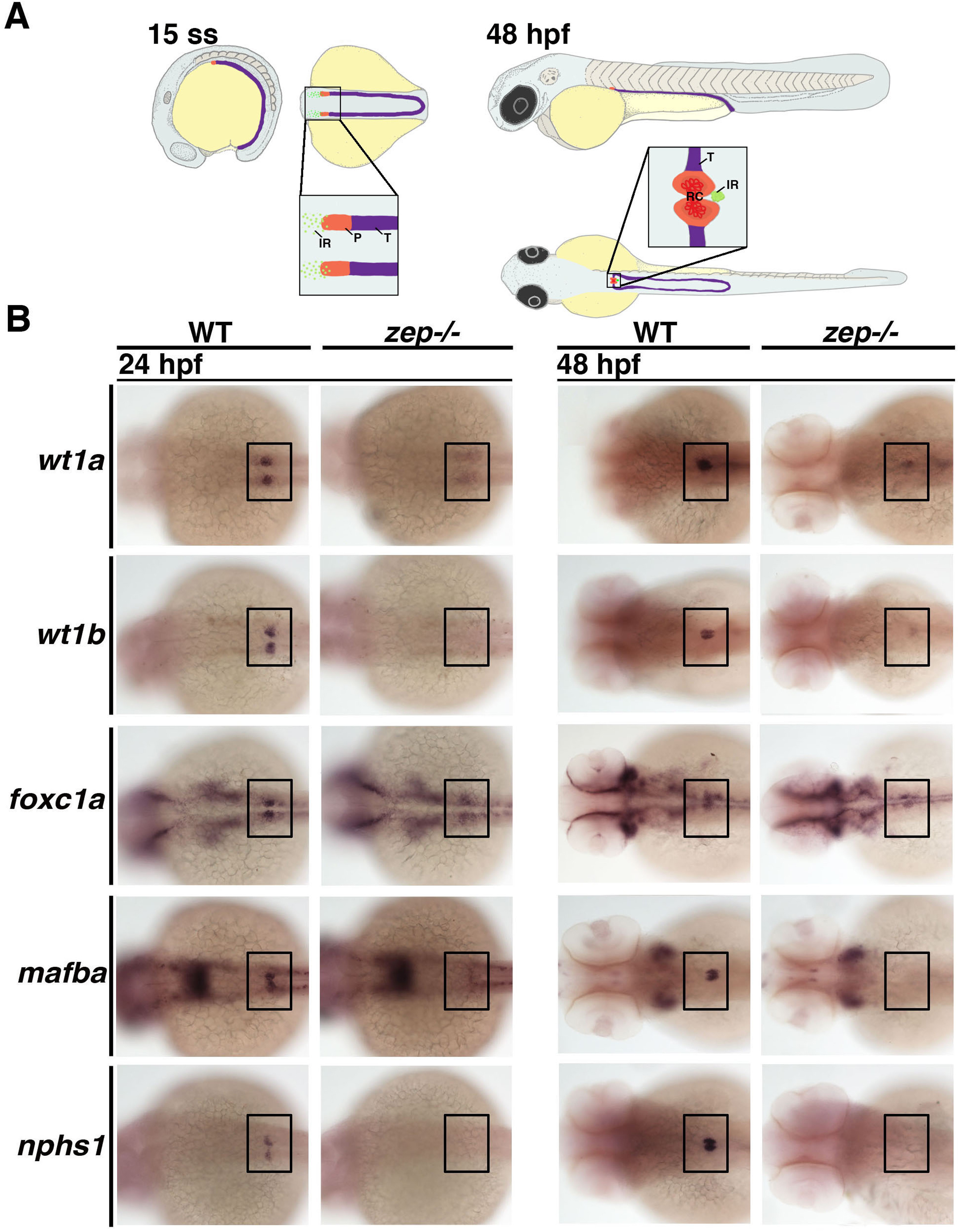
zepmutants fail to normally develop the podocyte lineage during nephrogenesis. (A) Location of podocyte and interrenal precursors and the result of their morphogenesis during early zebrafish embryonic development. (Left) The podocyte lineage (P, red) emerges rostral to the tubule lineages (T, purple) of the intermediate mesoderm at the 15 ss, while precursors of the interrenal gland (IR, green) are interspersed in the local vicinity of the podocyte precursors. (Right) By 48 hpf, morphogenesis events result in a single IR that is situated posterior to the fused glomeruli of the renal corpuscle (RC). Embryo drawings show lateral and dorsal views, with enlarged regions showing dorsal views. (B) Compared to WT siblings, zep mutant embryos have extremely reduced or absent expression of a suite of podocyte markers at the 24 and 48 hpf stages. Embryos are shown in dorsal views with each indicated gene expression stained in purple, where black boxes demarcate the cervical region where the podocytes develop.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 428(1), Kroeger, P.T., Drummond, B.E., Miceli, R., McKernan, M., Gerlach, G.F., Marra, A.N., Fox, A., McCampbell, K.K., Leshchiner, I., Rodriguez-Mari, A., BreMiller, R., Thummel, R., Davidson, A.J., Postlethwait, J., Goessling, W., Wingert, R.A., The zebrafish kidney mutant zeppelin reveals that brca2/fancd1 is essential for pronephros development, 148-163, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.