Fig. 1
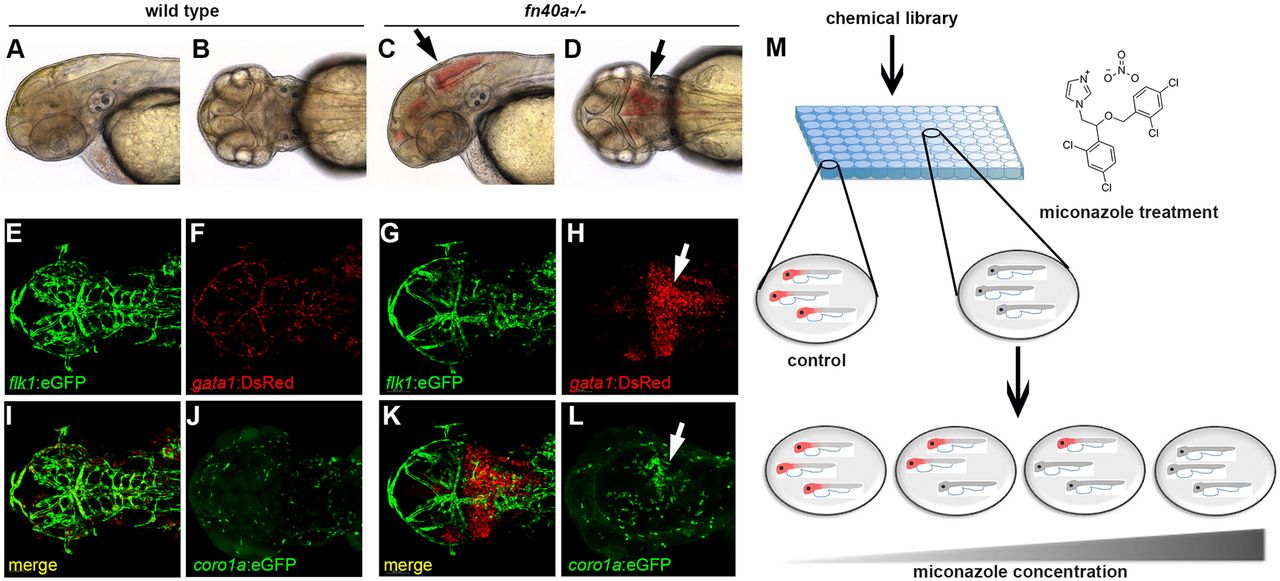
The fn40a mutant is a hemorrhagic stroke model suitable for chemical suppressor screens in zebrafish. (See also Figs S1,S2). (A-D) Live images of wild-type siblings (A,B) and homozygous fn40a mutants (C,D) at 2 dpf; note evident brain hemorrhages in the mutant (arrows). A,C: lateral view; B,D: dorsal view. (E-L) Live images of Tg(flk1:eGFP); Tg(gata1:DsRed) double transgenic embryos of wild-type siblings (E,F,I,J) and fn40a mutants (G,H,K,L) at 2 dpf. Note that gata1+ erythrocytes leak from Tg(flk1:eGFP)-labeled vessels and form hematomas in the mutants (G-H,K; arrow) while erythrocytes remain within vessels in wild-type siblings (E,F,I). Tg(coro1a:eGFP)-labeled macrophages and neutrophils accumulate at the hemorrhagic site in this mutant (L, arrow) whereas leukocytes are evenly distributed in the brain of a wild-type sibling embryo (J) at 2 dpf (n>8). (M) Overview of the chemical screen with mutant embryos arrayed in a 96-well plate and treated with DMSO or compound, illustrating that miconazole suppresses brain hemorrhages in a dose-dependent manner compared with DMSO treatment. Red color indicates hemorrhagic mutants.