Fig. 7
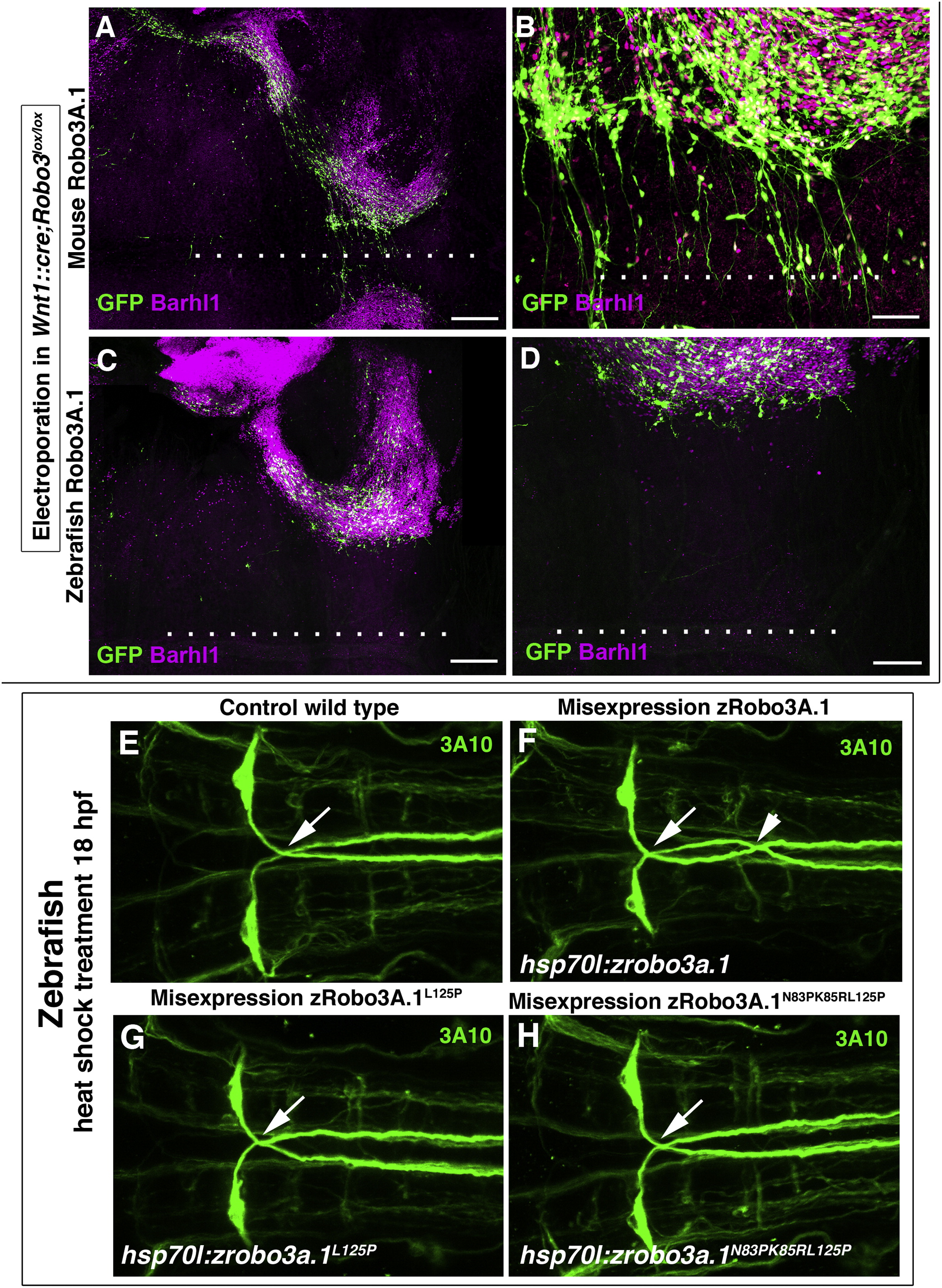
Rescue of Robo3−/− PN Neuron Midline Migration by Mammalian, but Not Nonmammalian, Robo3
(A and B) Rescue experiments by in utero electroporations of PN neurons in Wnt1::cre;Robo3lox/lox hindbrains coelectroporated at E13.5 with mouse Robo3A.1 and GFP, stained for PN marker Barhl1. Note that on the nonelectroporated side, Barhl1+ PN neurons do not migrate ventrally. By contrast, electroporated PN neurons and their axons reach the floor plate (dotted line) and/or cross it. (B) illustrates a higher magnification of the area near the floor plate.
(C) E17.5 Robo3−/− hindbrain coelectroporated at E13.5 with zebrafish Robo3A.1 and GFP. None of the electroporated PN neurons or their axons leave the abberant migratory stream and/or reach the midline (dotted line).
(D) Illustration of a higher magnification of the area near the floor plate.
(E–H) Dorsal views of confocal z-projections of the hindbrain of 72 hpf zebrafish embryos labeled with 3A10 antibody. Anterior is toward the left. Normal midline crossing of MA axons in control (E), hsp70l:zrobo3a.1L125P (G) and hsp70l:zrobo3a.1N83PK85RL125P (H) embryos. In hsp70l:zrobo3.1 embryos, extra midline crossing events of MA axons are shown in (F). The arrows in (E) through (H) indicate normal midline crossing of MA axons; the arrowhead in (F) points to an extra MA axon midline-crossing event.
Scale bars, 250 μm in (A); 50 μm in (B) and (E); 300 μm in (C); and 150 μm in (D). See also Figures S6 and S7.