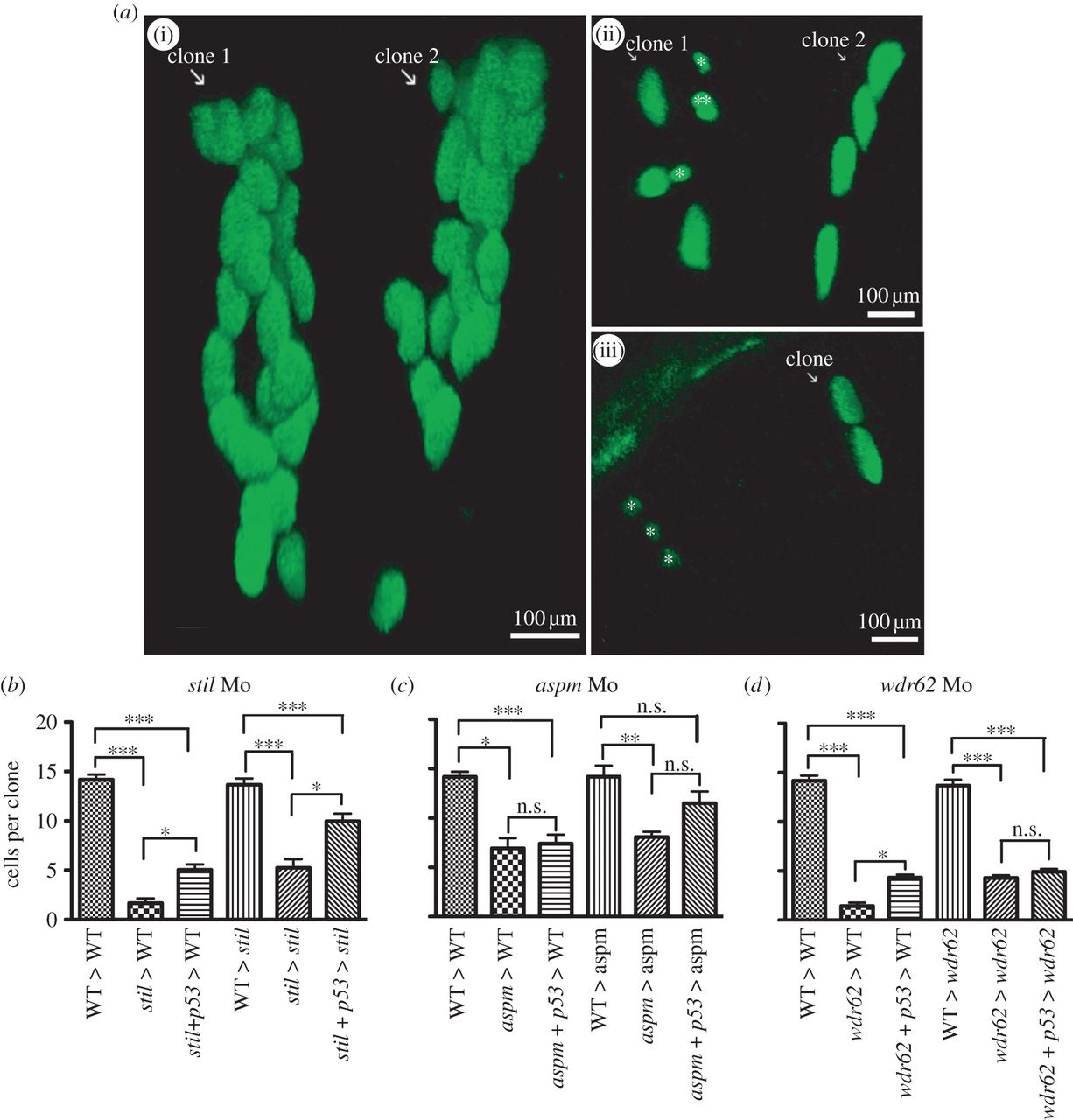
Fig. 5
Morpholino knockdown of stil, aspm or wdr62 led to reduced clonal proliferation of retinal progenitors in vivo. Blocking apoptosis only partially rescued clonal potential. Cells from H2B-GFP-expressing wild-type (WT) or morphant donor embryos were transplanted into WT or morphant host embryos at approximately 3.5 hpf. Host embryo retinas were screened for GFP-expressing one to two cell clones at 24 hpf and those clones were analysed again at 48 hpf. Graphs (b-d) show the mean cells per clone at 48 hpf (derived from a single cell at 24 hpf). The average size of retinal clones derived from WT cells in WT hosts was 14.2 cells (n = 73). (a)(i) Two typical WT clones in a WT host retina at 48 hpf, each derived from a two-cell clone identified at 24 hpf. No significant difference in clone size was seen when cells from control embryos were transplanted into WT environments (not shown): CoMo: 13.9 cells (n = 7) versus WT: 14.2 cells (n = 73) (p > 0.05). (b) stil morphant cells had a markedly reduced clonal capacity in WT hosts: stil Mo 1.7 cells (n = 8) versus 14.2 cells for WT (n = 73) (p < 0.001). Partial rescue of clone size was achieved with injection of anti-p53 Mo to block apoptotic cell death: stil + p53 Mo donor cells in WT hosts: 5.1 cells (n = 25) versus 1.7 cells without p53 Mo (n = 8) (p > 0.05). However, clones remained significantly smaller than WT: 5.1 cells (n = 25) versus 14.2 cells (n = 73) (p < 0.001). A similar result was seen when WT or stil morphant cells were transplanted into stil morphant hosts. Within the morphant environment, stil morphant cells produced smaller retinal clones compared with WT cells: 5.2 cells (n = 9) versus 13.7 cells (n = 27) (p < 0.001). (a)(ii) A typical example of morphant cell clones within a morphant host environment at 48 hpf. GFP-expressing cells from a stil morphant donor were transplanted into a stil morphant host. Clone 1 contains seven cells with one cell (marked double asterisks (**)) presumed to be undergoing mitosis at the time of imaging. In addition, two small cells that appear to be shrinking (marked single asterisk (*)) were presumed to be undergoing apoptotic cell death. Clone 2 contains four cells. Partial rescue of clone size could be achieved by injection of anti-p53 Mo to block apoptotic cell death: stil + p53 Mo donor cells in stil hosts: 10.0 cells (n = 31) versus 5.2 cells (n = 9) (p < 0.05). However, clones remained significantly smaller than WT clones: 10.0 cells (n = 31) versus 13.7 cells (n = 27) (p < 0.001). (c) aspm morphant cells also produced smaller clones than WT cells; 6.9 cells (n = 3) versus 14.2 cells (n = 73) (p < 0.05). Partial rescue of clone size could be achieved by injection of anti-p53 Mo: aspm + p53 Mo donor cells in WT hosts: 7.4 cells (n = 20) versus 6.9 cells without p53 Mo (n = 3) (p > 0.05). However, clones remained significantly smaller than WT: 7.4 cells (n = 20) versus 14.2 cells (n = 73) (p < 0.01). Within the morphant environment, aspm morphant cells produced smaller retinal clones than WT cells: 8.1 cells (n = 15) versus 14.2 cells (n = 12) (p < 0.01). Partial rescue of clone size could be achieved with injection of anti-p53 Mo: aspm + p53 Mo donor cells in aspm hosts: 11.5 cells (n = 14) versus 8.1 cells (n = 15); p < 0.05. However, clone size still remained smaller than WT clones: 11.5 cells (n = 14) versus 14.2 cells (n = 12) (p > 0.05). (d) wdr62 morphant cells also produced smaller clones than WT; 1.5 cells (n = 12) versus 14.2 cells (n = 73) (p < 0.001). (a)(iii) A typical example of morphant cell clones within a WT host environment at 48 hpf. GFP-expressing wdr62 morphant cells were transplanted into WT host embryos. Two clones are seen, derived from two single cells identified at 24 hpf. One clone (white arrow) contains two cells. The second clone consists of three small cells (marked single asterisk (*)), all presumed to be undergoing apoptotic cell death. Partial rescue of clone size was achieved by injection of anti-p53 Mo: wdr62 + p53 Mo donor cells in WT hosts: 4.3 cells (n = 40) versus 1.4 cells without p53 Mo (n = 12) (p < 0.05). However, clones remained significantly smaller than WT clones: 4.3 cells (n = 40) versus 14.2 cells (n = 73) (p < 0.001). Within the morphant environment, wdr62 morphant cells produced smaller clones than WT cells: 4.3 cells (n = 26) versus 13.7 cells (n = 18) (p < 0.001). No significant rescue was achieved by injection of anti-p53 Mo to block apoptotic cell death: wdr62 + p53 Mo donor cells in wdr62 hosts: 4.9 cells (n = 28) versus 4.3 cells (n = 26) (p > 0.05). Clone size remained significantly smaller than WT clones: 4.9 cells (n = 28) versus 13.7 cells (n = 18) (p < 0.001). n = number of surviving clones examined at 48 hpf.