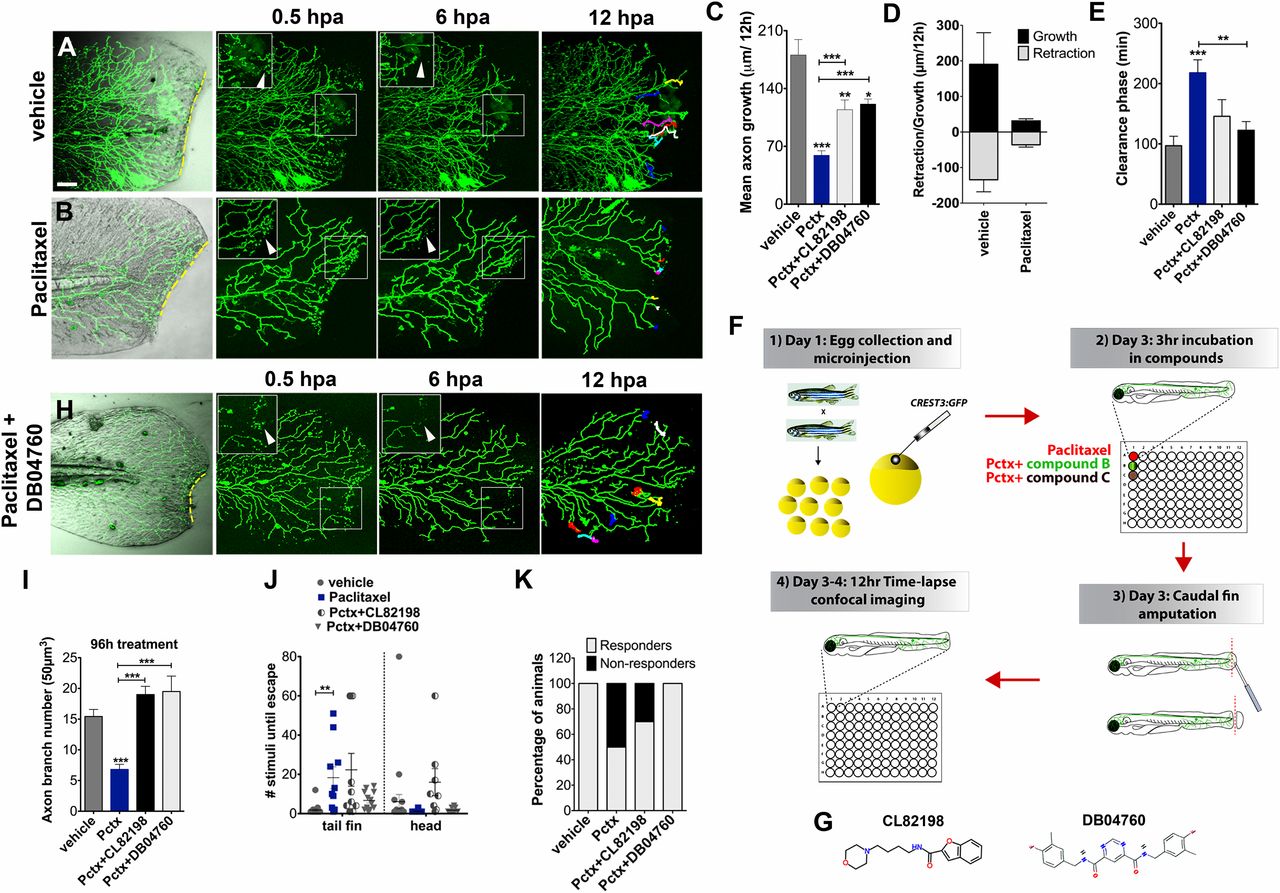
Fig. 4
Paclitaxel-induced neurotoxicity in larval fish is attenuated by MMP-13 inhibition. (A and B) Cutaneous branches of a single-labeled RB neuron were traced for 12 h in the caudal fin following fin amputation. Larvae were incubated for 3 h either in vehicle solution (0.5% DMSO/Ringers) (A) or paclitaxel (22 µM) (B). Insets show higher magnification of boxed regions (arrowheads depict axon debris lost in vehicle but not paclitaxel-treated animals). Tracks in the last panel depict branch growth over time. (C) Quantification of mean axon branch growth over 12 h in larvae incubated in vehicle, paclitaxel (22 µM), and paclitaxel plus either DB04760 or CL-82198 (10 µM each) (n = 3, 3-4 fish per group). (D) Comparison of mean axon growth and retraction in injured vehicle and paclitaxel-treated animals over 12 h (n = 2, 3-4 fish and 15 axons per group). (E) Quantification of axon debris clearance (n = 2, 3-4 fish and 5-7 axons per group). (F) Scheme of compound screening assay. (G) Chemical structures of MMP-13 inhibitors. CL-82198, N-[4-(4-morpholinyl)butyl]-2-benzofurancarboxamide; DB04760, N4,N6-bis[(4-fluoro-3-methylphenyl)methyl] pyrimidine-4,6-dicarboxamide. (H) Axon regeneration is partially restored with 10 µM DB04760 (arrowheads mark diminishing axon debris). (I) Comparison of axon branch density following 96 h of treatment (n = 2, 5 fish per group). (J) Touch response in fin and head region after 96 h of treatment (n = 4, 5 fish per group). (K) Percentage of animals with improved touch response upon coadministration of paclitaxel and either CL-82198 or DB04760. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (Scale bar, 50 µm.) hpa, hours postamputation; Pctx, paclitaxel.