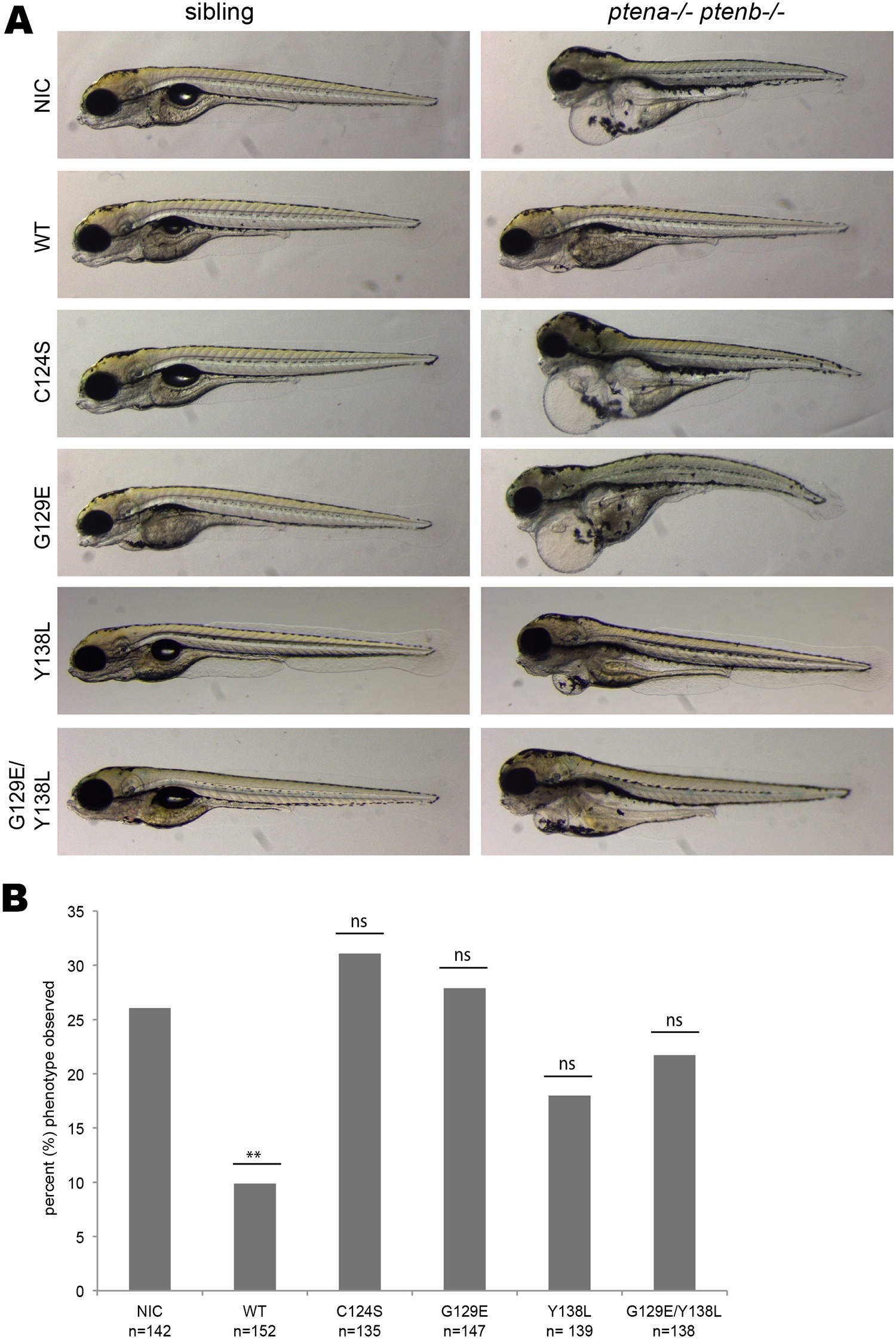
Fig. 2
Both Pten phosphatase activities are required to rescue the ptena-/-ptenb-/- pleiotropic phenotype.
Zebrafish embryos from a ptena+/- ptenb-/- incross were injected with either wild type Ptenb-mCherry, Ptenb-mCherry C124S, Ptenb-mCherry G129E or Ptenb-mCherry Y138L encoding synthetic mRNA at the one-cell stage. (A) At 4 dpf the embryos were submitted to brightfield microscopy and analyzed for the pleiotropic phenotype. Pictures show representative, genotyped embryos. Non-injected control embryos (NIC) were included for reference. (B) Quantification of the embryos showing the typical ptena-/-ptenb-/- pleiptropic phenotype at 4dpf. In the non-injected control (NIC), approximately 25% of the embryos showed the characteristic phenotype (Mendelian segregation). Only wild type Ptenb-mCherry rescued the pleiotropic ptena-/-ptenb-/- phenotype significantly at 4dpf. The statistical significance of each of the conditions compared to the non-injected control was determined using two-tailed Fisher’s exact test and is indicated in the bar graph (ns = not significant, * = p-value < 0,05, ** = p-value < 0,01, *** = p-value < 0,001).