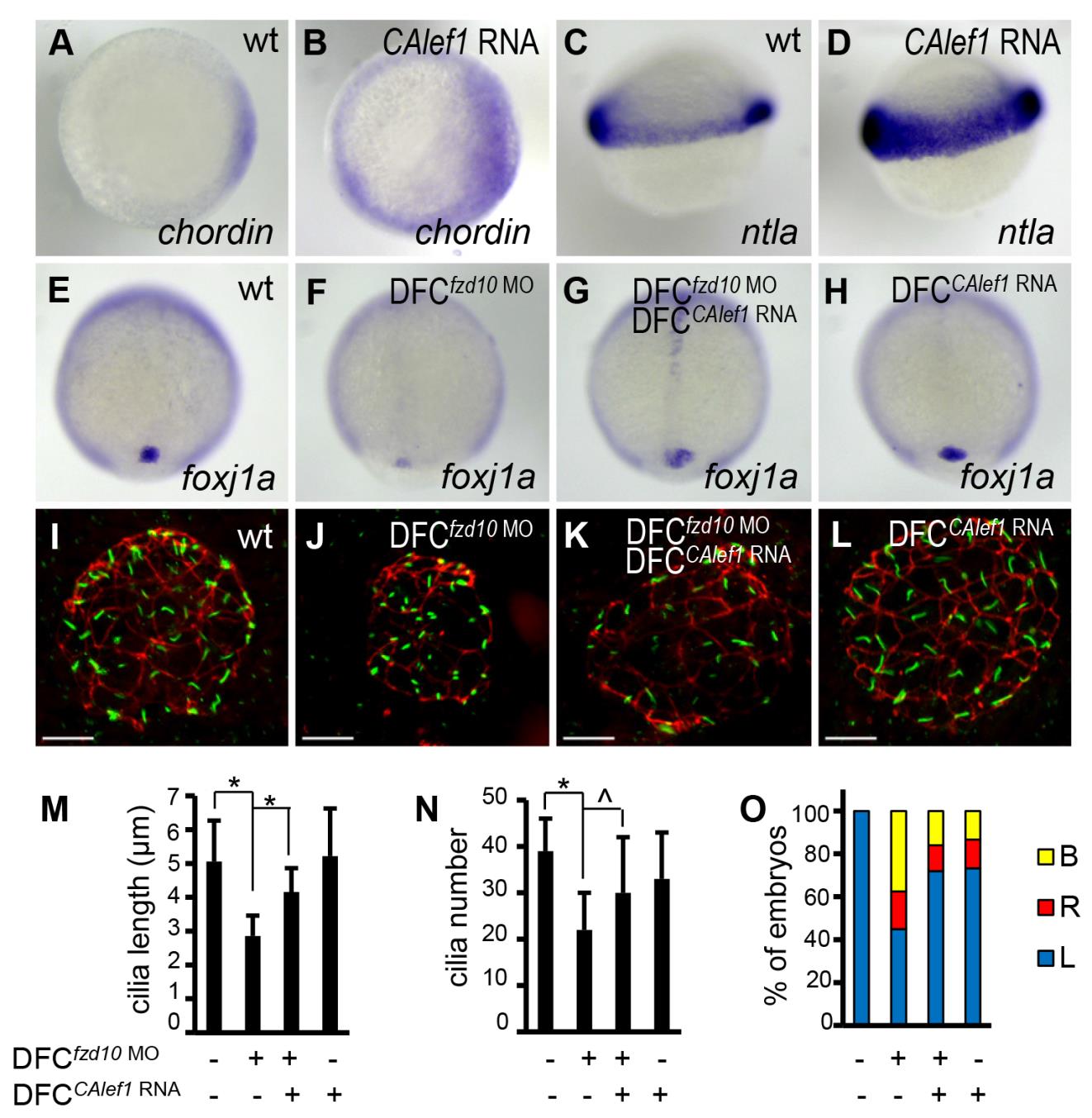
Fig. S4 KV-specific expression of CALef1 rescues ciliogenesis and LR asymmetry defects in DFCfzd10 MO embryos. (A-D) Expression of CALef1 activates Wnt target gene expression. Injection of CAlef1 mRNA (100 pg) into 1-cell staged embryos expanded the expression of Wnt target gene chordin (B) and ntla (D). Shown are dorsal views (A and B) and lateral views (C and D) of 30%-epiboly staged embryos. (E-H) Ectopic expression of CALef1 rescues foxj1a levels in DFCfzd10 MO embryos. DFC-targeted injection of fzd10 MO (4 ng) downregulated foxj1a expression (F; 28/29). This downregulation was rescued by DFC-targeted CAlef1 mRNA injection (100 pg) (G; 20/30). Overexpression of CALef1 alone had no apparent effect on steady state foxj1a expression (H). (I-L) Ectopic expression of CALef1 rescues ciliogenesis in DFCfzd10 MO embryos. DFC-targeted injection of fzd10 MO (4 ng) reduced both cilia length and number (J). Coinjection of CAlef1 mRNA (100 pg) with fzd10 MO (4 ng) partially restored cilia length and number (K). Ectopic expression of CALef1 alone had no apparent effect on cilia length and number (L). Cilia were visualized by anti-acetylated α-tubulin staining (green) and apical-basal polarity of KV cells by anti-ZO-1 staining (red) in 10-somite staged embryos. (M and N) Quantification of cilia length (M) and number (N). Approximately 18 to 23 embryos were analyzed for each group. Data are represented as mean mean ± s.d. (O) Ectopic expression of CALef1 partially rescues left-sided spaw expression in DFCfzd10 MO embryos. Percentage of embryos with specific spaw expression patterns was determined in 21- somite staged embryos; 40 to 96 embryos per group were scored. B indicates bilateral; L, left side; R, right side. * indicates P<.01, and ^ indicates P<.05. Scale bar: 20 µm.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Biol. Open