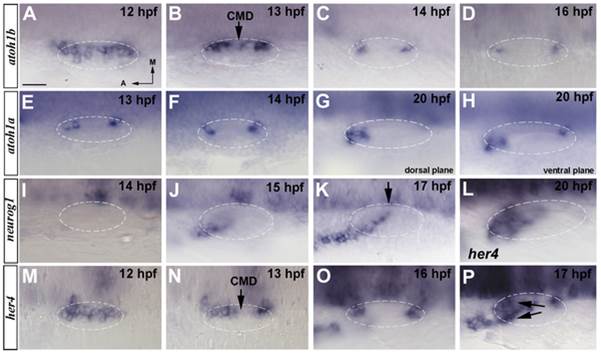
Fig. 1 Spatiotemporal expression of proneural genes at early stages of inner ear development.
(A–D) In situ hybridization in wild-type embryos for atoh1b. atoh1b is expressed in a large medial domain adjacent to the hindbrain at 12 hpf (A) to then progressively restrict to two patches that correspond to the future anterior and posterior prosensory domains (B–D). Between 13 hpf and 14 hpf atoh1b is downregulated at the central medial domain (CMD) (arrow in B). (E–H) In situ hybridization in wild-type embryos for atoh1a. atoh1a is expressed in the anterior and posterior sensory domains by 13 hpf and 14 hpf (E, F). At 20 hpf the expression in the anterior domain increases (G) and just two positive cells remain in the posterior (H). (I–K) In situ hybridization in wild-type embryos for neurog1. Expression of neurog1 in the inner ear starts at 15 hpf (J) and it is extended from an anterolateral position to a posteromedial domain (K). neurog1 progressively invades the CMD (arrow in K). (L–P) In situ hybridization in wild-type embryos for her4. her4 expression is found at 12 hpf (M) to become restricted to the future sensory maculae by 13 hpf (N). At 16 hpf her4 presents higher expression levels (O) and at 17 hpf, the expression of her4 appears in the neurogenic domain being a sum of the expressions from both domains (arrows in P). By 20 hpf the expression only remains at the anterior sensory domain (L). Dorsal views; anterior to the left, medial to the top. Dashed circles delineate otic vesicles. All images are at same magnification. Scale bar: 25 µm.