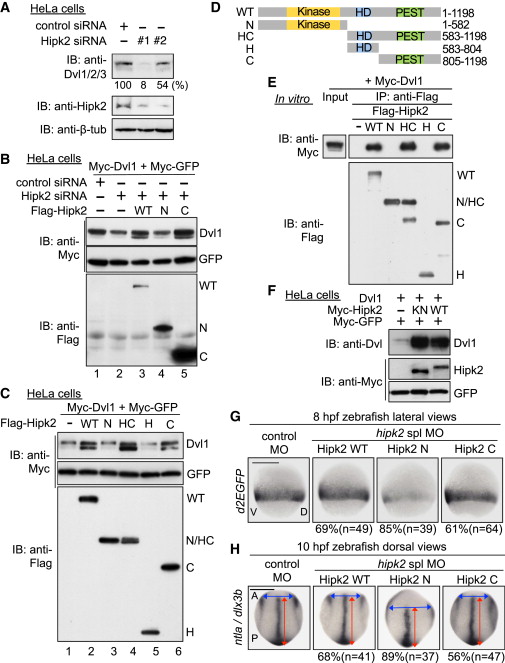
Fig. 2 Hipk2 Regulates Dvl Stability in a Kinase Activity-Independent Manner in Mammalian Cells and Zebrafish
(A) Hipk2 is required for endogenous Dvl stability in HeLa cells. Cells were treated with either control siRNA or Hipk2 siRNA #1 or #2, and cell extracts were then were immunoblotted with anti-Dvl1/2/3 (which recognizes all types of Dvl), anti-Hipk2, and anti-β-tubulin (7beta;-tub). β-tub was used as a loading control. Relative Dvl protein levels were calculated by determining the ratio of Dvl to β-tub. Values are presented below the top panel as the relative percentage.
(B) Hipk2 WT and C, but not Hipk2 N, reversed the Hipk2-knockdown-induced reduction in Dvl expression. HeLa cells were treated with either control siRNA or Hipk2 siRNA#1 and then transfected with Myc-Dvl1 and Myc-tagged GFP (Myc-GFP) with or without Flag-tagged human Hipk2 (Flag-Hipk2) WT, N, and C.
(C) Hipk2 increased the Dvl protein levels via its C-terminal domain. HeLa cells were transfected with Myc-Dvl1 and Myc-GFP with empty vector () or Flag-Hipk2 WT, N, HC, H, or C.
(D) Schematic diagram of the human Hipk2 deletion mutants. Kinase, kinase domain; HD, homeodomain-interacting domain; PEST, PEST sequence.
(E) The C-terminal domain of Hipk2 is essential and sufficient for binding to Dvl. HeLa cells were transfected with empty vector () or Flag-tagged human Hipk2 (Flag-Hipk2) WT, N, HC, H, or C. The cell extracts were mixed with extracts prepared from cells transfected with Myc-Dvl1 and then immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag. Immunoprecipitated complexes were then immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. The expression of Myc-Dvl1 proteins in cell extracts was confirmed by immunoblotting with anti-Myc (“Input” lane).
(F) Hipk2 increases the protein level of Dvl1 in a kinase activity-independent manner. HeLa cells were transfected with Dvl1, Myc-tagged mouse Hipk2 (Myc-Hipk2) WT and KN, and Myc-GFP, as indicated.
(G and H) Hipk2 regulates the β-catenin pathway-mediated posterior mesoderm formation and CE via its C-terminal domain. Embryos were injected with MOs with or without human Hipk2 WT, N, or C mRNA. Panels show whole-mount in situ hybridization of d2EGFP in OTM:d2EGFP-transgenic zebrafish embryos (G) or ntla and dlx3b in nontransgenic zebrafish embryos (H) fixed at the indicated stages. The percentages of embryos showing similar expression patterns and total number of MO-injected embryos (n) are shown under each image.
See also Figures S2 and S3.