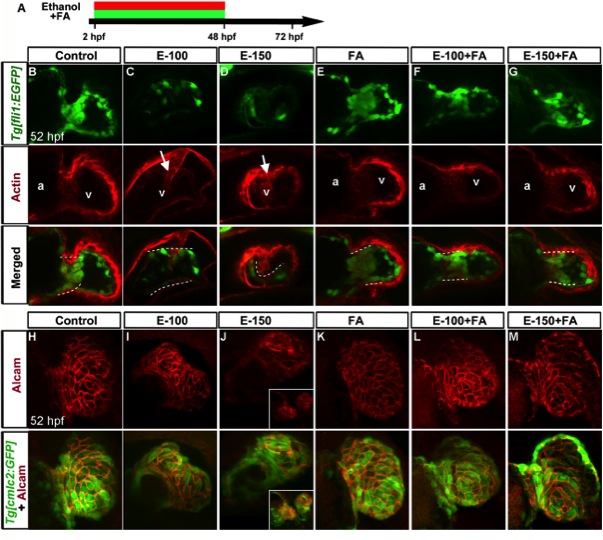
Fig. 9 Folic acid supplementation during chronic ethanol exposure (2–48 hpf) rescues ethanol-induced endocardial cushion and chamber formation defects. A: Schematic diagram showing the timing of ethanol and FA exposure. B–G: Endocardial cushion formation was restored in ethanol-exposed, FA co-supplemented embryos. Stained Tg[fli1:EGFP] embryos showed clustering of GFP- and F-actin-positive cells (white dashed line) in the control, FA-treated, and ethanol+FA-cotreated embryos. Ethanol-treated embryos exhibited no clustering of GFP- and F-actin-positive cells at the AV boundary. White arrow, defective wall in the ventricle. a, atrium; v, ventricle. Atrium in the ethanol-treated embryos cannot be seen in this view. H–M: Ethanol-induced ventricular chamber defects were rescued in the FA-cosupplemented embryos. Alcam-stained Tg[cmlc2:GFP] embryos showed a similar pattern of cardiomyocyte distribution in the ventricular wall of control, FA-treated, and ethanol+FA-cotreated embryos; cardiomyocyte sizes and shapes were variable throughout the ventricular wall in the ethanol-treated embryos. Inset (J) in 150 mM ethanol showed cardia bifida. Anterior to the top.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.