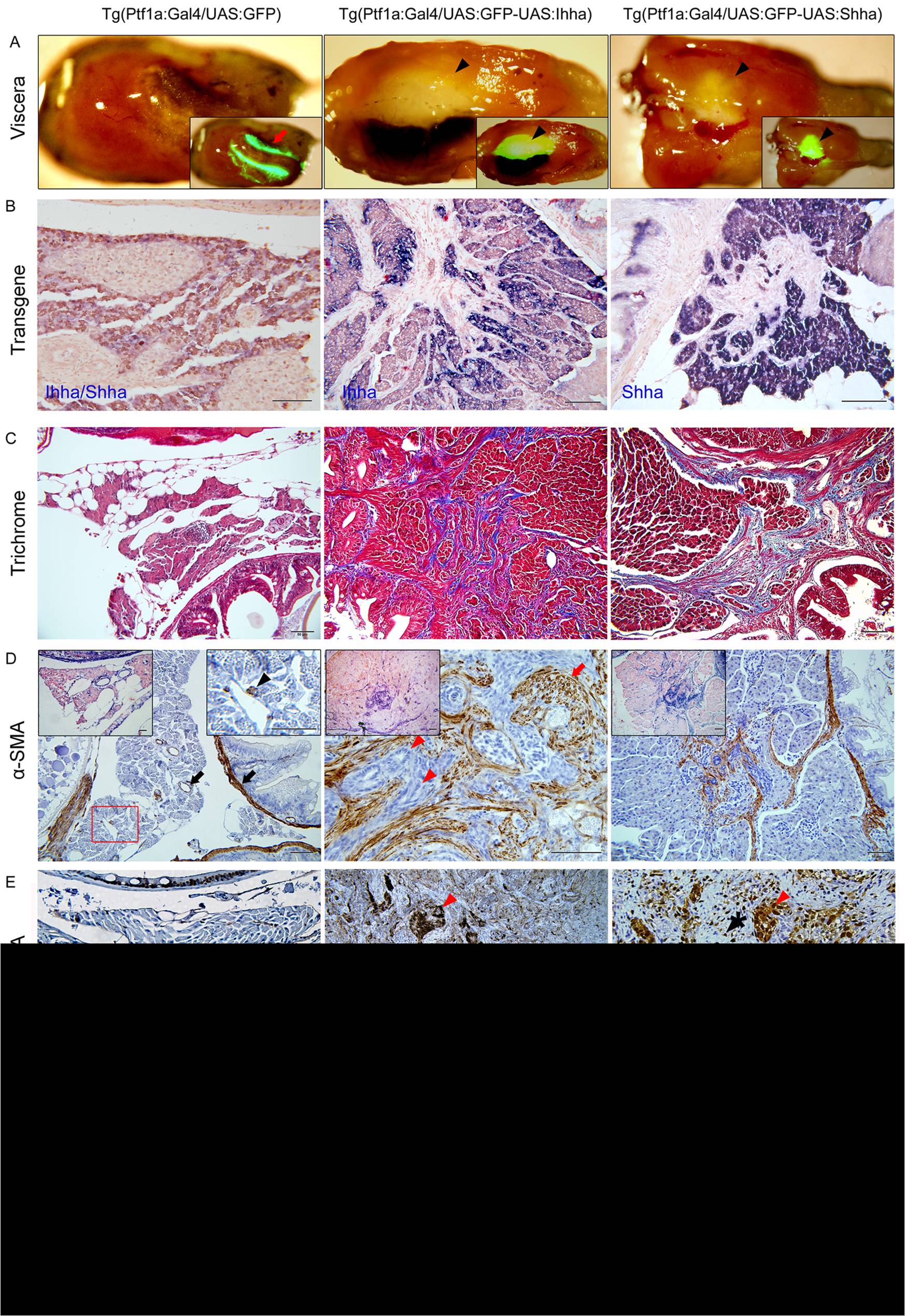
Fig. 4 Hh-induced pancreatic fibrosis and proliferation of myofibroblasts.
(A) Dissected whole viscera from 4 month-old zebrafish showing transgene (GFP) expression. Ventral views. Left, anterior. The pancreas of control appears as a thread-like structure between the bowel and visceral organs (arrow). In Hh ligand-expressing pancreas, prominent fibrosis around the principal islets forms whitish plaque-like lesions showing robust GFP expression (arrowheads). Inlets are merged in bright and fluorescence images. (B) ISH for transgene expression. The control pancreas reveals negligible expression of either Ihha or Shha. In the Hh-expressing pancreas, transgene expression is strictly restricted to acinar cells with nil expression at myofibroblasts or ductular cells. (C) Trichrome stains showing fibrotic bands. (D) IHC for α-SMA. Muscle layers of the bowel and large pancreatic ductal wall are reactive to α-SMA in control (black arrows). Infreqeuently, α-SMA-positive cells are noted (black arrowhead) in the parenchyme of control pancreas suggesting presence of stellate cells. Infilitrating myofibroblasts are invariably reactive to α-SMA while proliferating ductular cell are not (red arrowheads). Note the thickened and α-SMA-reactive intrapancreatic duct wall (red arrow). Left inlets (200×) are ISH images. Right inlet is an enlarged view of the box. (E, F) IHC for PCNA and pHH3. Within the fibrotic area, both ductular cells (red arrowheads) and myofibroblasts (black arrowheads) are frequently reactive to both PCNA and pHH3, suggesting enhanced proliferation. Intestinal crypt cells are also frequently reactive to both PCNA and pHH3 (black arrows) and used as internal control. If not specified, microscopic images are 400×. Bars, 50 μm.