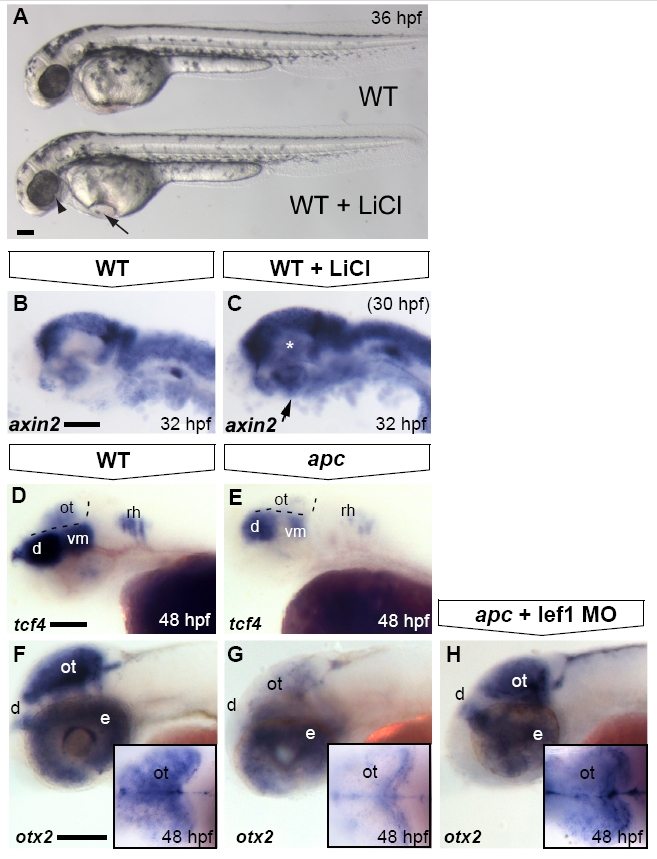
Fig. S4 Optic tectum phenotypes in apc mutants are mainly due to overactivated Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Lateral view. Anterior to the left. (A) LiCl treatments at late stages cause morphological defects in the eye (arrowhead), otic vesicles and heart (arrow) similar to the apc phenotype. (B, C) Upon late LiCl treatment at 30 hpf (C), the Wnt/β-catenin target gene axin2 is enhanced in the dorsal brain and induced in the ventral brain (n = 19; asterisk and arrow). (D, E). tcf4 is expressed in the OT of wild-types (D), whereas it is absent from the mutant tectum (n = 12; E) Dashed lines indicate MHB and ventral/dorsal midbrain boundary. (F–H) Loss of otx2 expression in the apc optic tectum is restored to near wild-type expression levels (H) upon Lef1 knockdown using 1 ng of lef1 MO (strong rescue in 50% of apc mutants; remaining mutants show weak induction; n = 23). Insets — dorsal view with eyes removed. d, diencephalon; e, eye; ot, optic tectum; rh, rhombomere; vm, ventral midbrain. Scale bar 125 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 331(2), Paridaen, J.T., Danesin, C., Elas, A.T., van de Water, S., Houart, C., and Zivkovic, D., Apc1 is required for maintenance of local brain organizers and dorsal midbrain survival, 101-112, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.