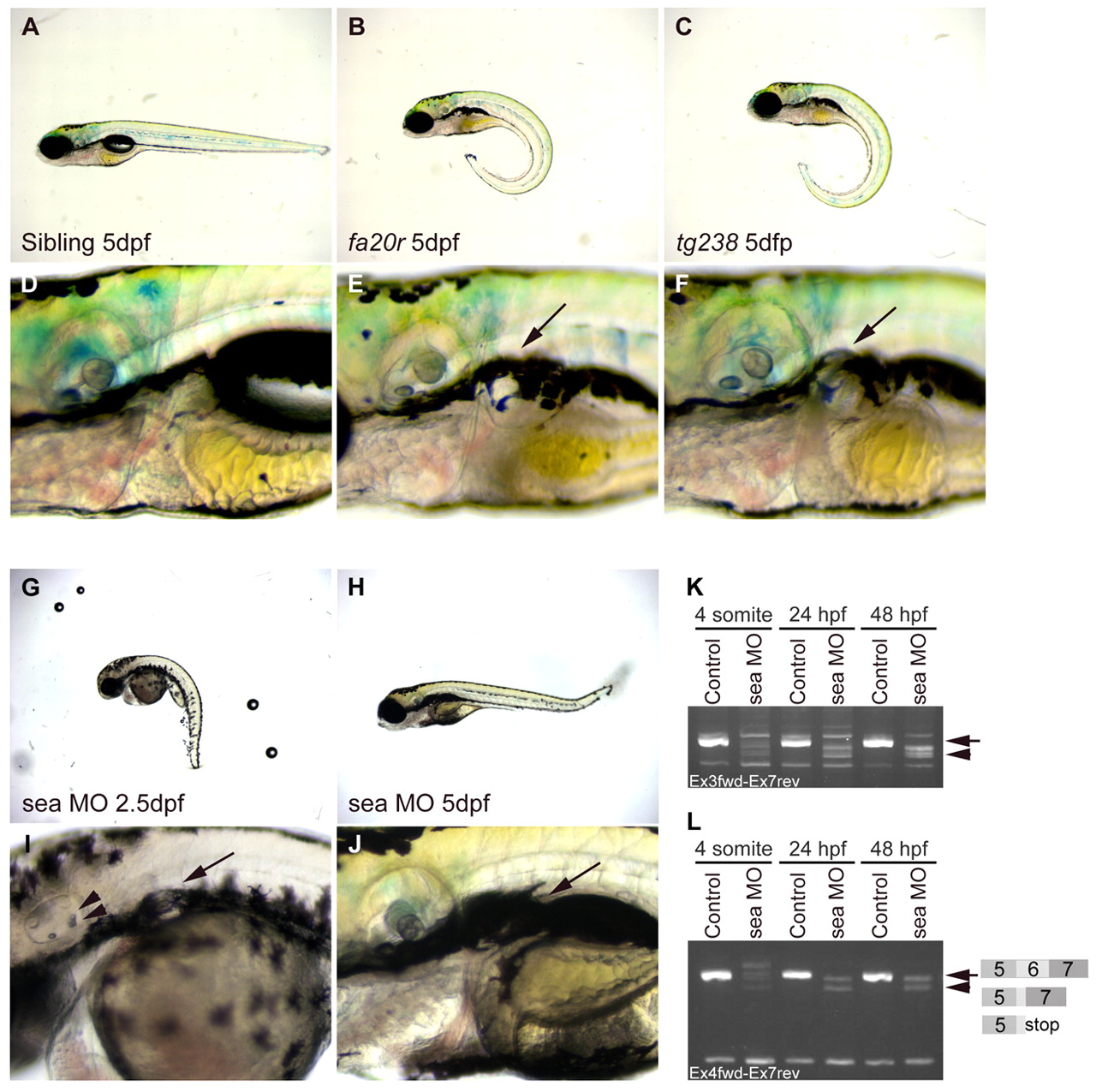
Fig. 2 seahorse mutants and sea MO-injected embryos displayed curly tail down and pronephric cyst phenotypes. (A-F) CTD and pronephric cyst phenotypes in sea mutants. (A) Siblings, (B) seafa20r and (C) seatg238a; mutant embryos have CTD phenotypes at 5 dpf. (D) Siblings, (E) seafa20r and (F) seatg238a embryos at higher magnification to show pronephric cysts at 5 dpf (arrows). (G-J) CTD and pronephric cyst phenotypes in sea MO-injected embryos. MO-injected embryos can recover from the CTD (H) and cyst phenotypes (J) by 5 dpf. Defects in otic vesicle and otolith formation (arrowheads) were observed in some sea MO-injected embryos (I). (K,L) RT-PCR from uninjected and sea MO-injected cDNA libraries at four somites, 24 hpf and 48 hpf. (K) Primers between exon 3 and exon 7 amplified a wild-type sea band at 635 base pairs (bp; arrow) and incorrectly spliced message in sea MO-injected embryos (arrowhead). (L) Primers between exon 4 and exon 7 amplified a wild-type sea band at 517 bp (arrow; exon 5-7) and incorrectly spliced message in sea MO-injected embryos (arrowhead). Incorrect splicing generated two main splice forms creating either a deletion and/or stop codon in exon 6 (indicated by the diagram in L).
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development