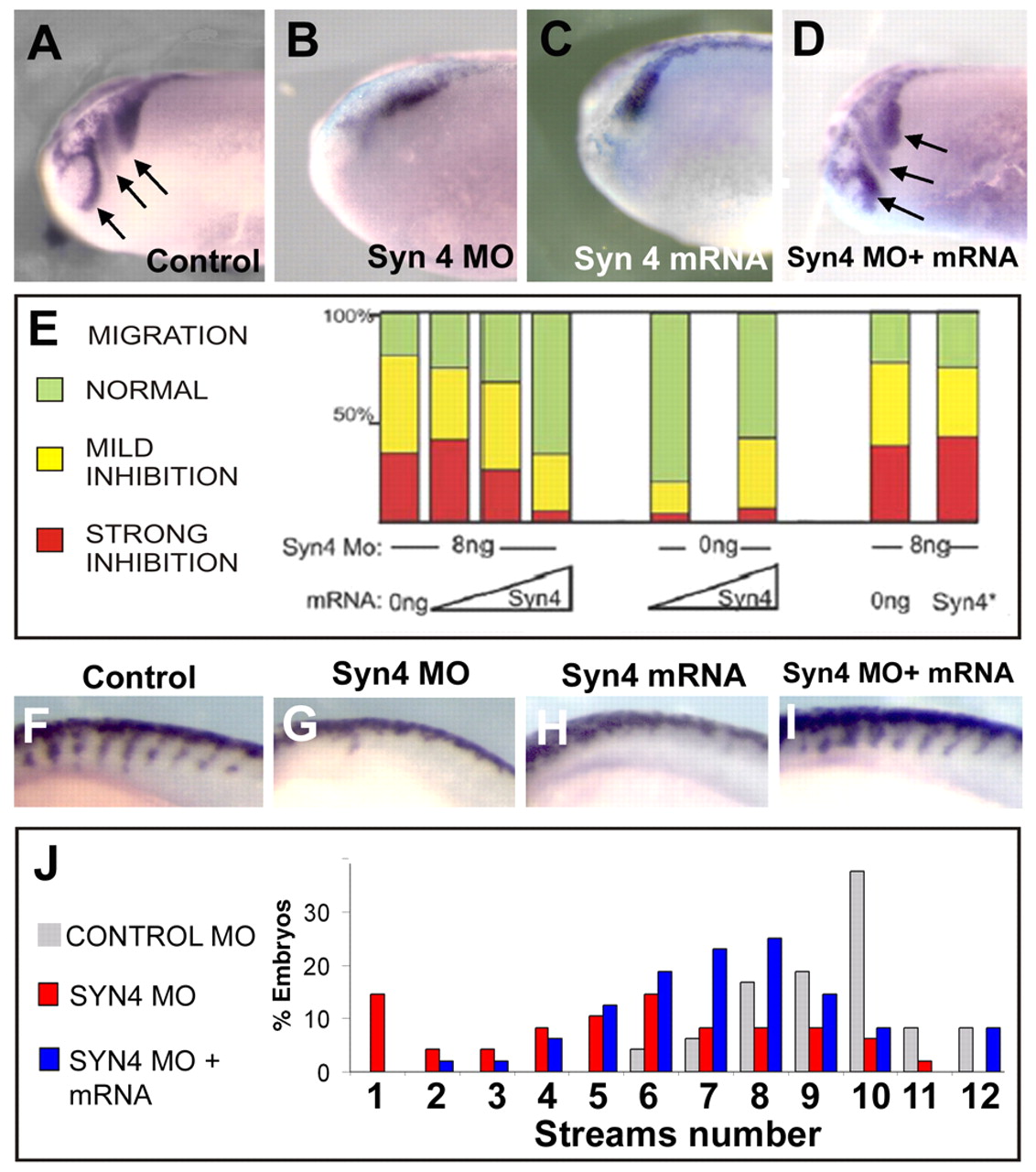
Fig. 3 Syn4 is required for NC migration. (A-D) Lateral view of Xenopus cephalic NC at stage 24, analyzed by the expression of snail2. Arrows indicate streams of migrating NC. (A) 8 ng control MO; (B) 8 ng syn4 MO; (C) 100 pg syn4 mRNA; (D) 8 ng syn4 MO and 100 pg syn4 mRNA. (E) Xenopus embryos were injected with 8 ng of syn4 MO together with 0, 25, 50 or 100 pg of syn4 mRNA (1st to 4th bar), 50 or 100 pg of syn4 mRNA only (5th and 6th bar), or 8 ng syn4 MO with 0 or 150 pg of syn4 mRNA mutated in the PKCα-binding site (Syn4*, 7th and 8th bar). NC migration was analyzed by the expression of snail2 at stage 24, as shown in A. Embryos were scored as a normal migration, mild or strong inhibition. Co-injection of syn4 mRNA rescues the inhibition of NC migration produced by the syn4 MO (1st to 4th bar), but no rescue is observed with Syn4 mutated in the PKCα-binding site (Syn4*, 7th and 8th bar). (F-I) Lateral view of zebrafish at 20 somites. Trunk NC migration was analyzed by the expression of crestin. Dorsal to the top; anterior to the left. (F) Control MO (6 ng); (G) syn4 MO (6 ng); (H) syn4 mRNA (250 pg); (I) syn4 MO and syn4 mRNA. (J) NC migration was analyzed by the expression of crestin when the embryo had 20 somites. The number of streams of NC migrating through the somites was counted. Co-injection of syn4 mRNA rescues the reduction in the number of streams of NC produced by syn4 MO.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development