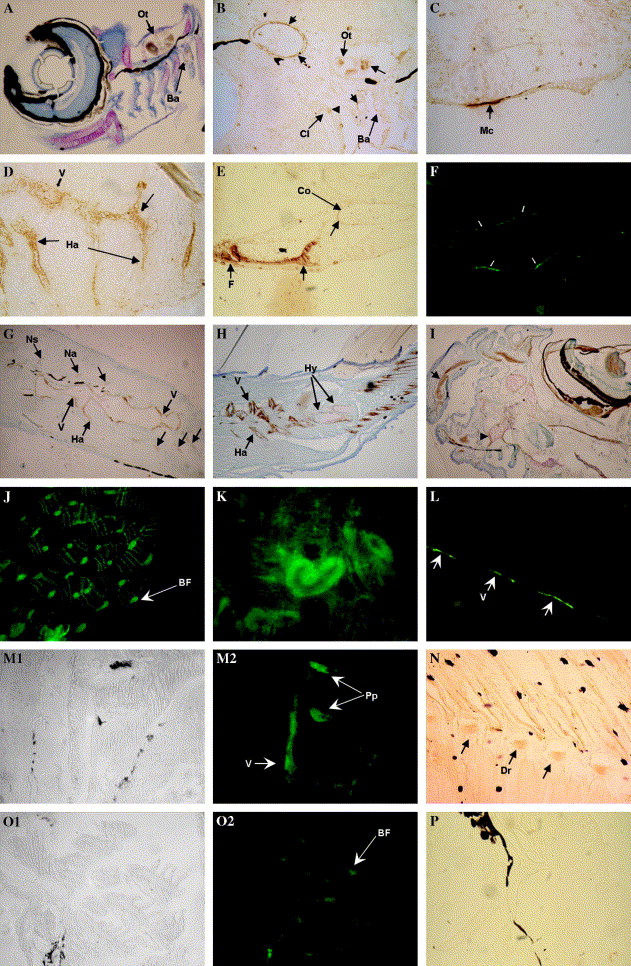
Fig. 4 Immunohistochemical and immunofluorescent detection of Bgp accumulation at different developmental stages. (A–K) Bgp in zebrafish. (A) Accumulation of Bgp in the teeth of branchial arch 5 (Ba) and otolith (Ot) of a 8 dpf larva (200×); counterstaining with toluidine blue. (9B) Accumulation of Bgp in the teeth of branchial arch 5, otolith and cleithrum of a 9 dpf larva (400×). (C) Accumulation of Bgp in Meckel’s cartilage of a 13 dpf larva (1000×). (D) Accumulation of Bgp is first detected in calcifying vertebra and hemal arches at 13 dpf (1000×). (E) Accumulation of Bgp in the calcifying pectoral fin (F) and coraco–scapular complex (Co) at 20 dpf (400×). Notice the accumulation at the periphery of the coracoid undergoing perichondral mineralization. (F) Immunofluorescent detection of Bgp accumulation in the mineralizing urostile at 20 dpf (400×). (G) Accumulation of Bgp in the vertebral column (V), neural arches (Na), neural spines (Ns), and hemal arches (Ha) at 20 dpf (200×). (H) Bgp accumulation in the vertebral column, hemal arches, and in the mineralizing matrix of hypural plates (Hy) of the caudal fin and in the mineralized fin rays of a 31 dpf juvenile (100×). (I) Accumulation of Bgp in a juvenile is detected in all the bones and calcifying cartilages of the head region, e.g., supramaxillary (arrow) and associated bones, the ethmoid plate (arrowhead), and the supra orbital cartilage that surrounds the eye (100×). (J) Accumulation of Bgp is widely detected by immunofluorescence in the branchial arches of a juvenile (200×). (K) Bgp accumulation in epithelial cells from some renal tubules of the kidney in juveniles (400×). (L–P) Bgp in sole. L-Immunofluorescent detection of Bgp in the forming vertebra (arrows) surrounding the notochord of a 15 dpf larvae (400×). (M) Detection of Bgp accumulation in the vertebra and parapophysis (Pp) at 25 dpf (M1 bright field and M2 dark field) (250×). (N) Accumulation of Bgp in the calcifying distal radials (Dr) at 25 dpf. (O0 Bgp is strongly detected in the calcified branchial arches of a 41 dpf juvenile (O1 bright field and O2 dark field) (250×). (P) Control immunohistochemical detection with pre-immune serum lacks staining, shown here in cranial bones of a 20 dpf larvae.
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 6(6), Gavaia, P.J., Simes, D.C., Ortiz-Delgado, J.B., Viegas, C.S., Pinto, J.P., Kelsh, R.N., Sarasquete, M.C., and Cancela, M.L., Osteocalcin and matrix Gla protein in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Senegal sole (Solea senegalensis): Comparative gene and protein expression during larval development through adulthood, 637-652, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns