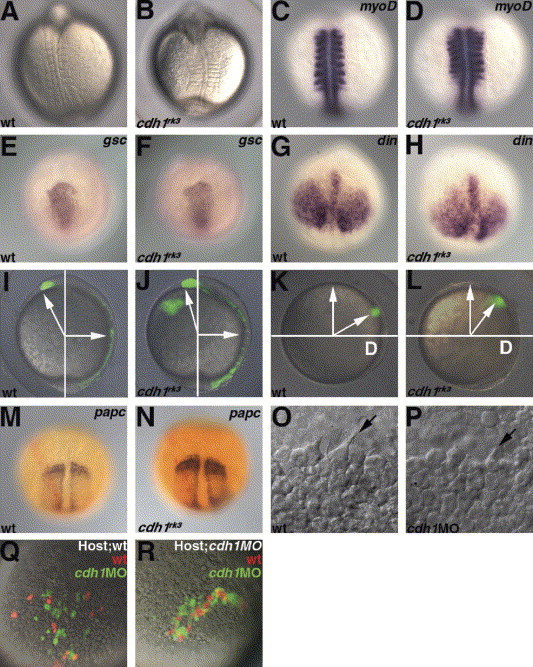
Fig. 6 Impaired gastrulation cell movements in the cdh1rk3 mutants. (A, B) Dorsal views of the wild-type and the zygotic cdh1rk3 mutant embryos at the ight-somite stage. (C, D) Expression of myoD in the wild-type and the cdh1rk3 mutant embryos at the eight-somite stage. Dorsal views. (E–H) Expression of goosecoid (gsc) and chordin (din) in the wild-type (E, G) and the cdh1rk3 mutant embryos at 8.5 hpf. Animal pole views with dorsal to the bottom (E, F) and dorsal views with anterior to the top. (I–L) Impaired convergence and extension. Cells in the embryonic shield (I, J) or cells at the lateral blastoderm margin (90 °C from the dorsal side, K, L) in wild-type (I, K) and cdh1rk3 mutant (J, L) embryos were labeled by uncaging fluorescein dextran with ultraviolet light at the shield stage. The position of the labeled cells was determined at 10 hpf. Lateral views with dorsal to the right (I, J), and vegetal pole views with dorsal to the right (K, L). The angles for the anterior movements (extension and migration) of the anterior mesendoderm were 121.8±4.3° (average±SD, n=8) in the wild-type and 110.8±4.4° (n=5) in the cdh1rk3 mutant embryos. The angles for the convergence movements of the lateral blastoderm margin were 59.4±5.9° (n=7) in the wild-type and 50.7±11.2° (n=7) in the cdh1rk3 mutant embryos. Embryos in which the lateral blastoderm margin was labeled were fixed at 10.5 hpf (the two-somite stage for wild-type) and stained with papc riboprobe (purple) and anti-fluorescein antibodies (red) (M, wild-type; N, cdh1rk3 mutant). (O, P) DIC images of the anterior axial mesendoderm in the wild-type (O) and cdh1 morphant mutant embryos (P) at 8.5 hpf (80% epiboly for the wild-type). The filopodia formation (arrows) of the anterior axial mesendoderm was observed in both the wild-type and the cdh1 morphant embryos. (Q, R) Transplantation of wild-type and Cdh1-defective cells into wild-type (Q) and cdh1 morphant embryos (R). Cells in the blastoderm margin were isolated from wild-type control (marked by Alexa Fluor 568 dextran, red) and cdh1 morphant (marked by fluorescein dextran, green) embryos and transplanted into the ventral margin of shield stage wild-type embryos. The locations of the control and the cdh1 morphant cells were determined at 9 hpf. Both the transplantation experiments were carried out nine times and the representative data were shown. Ventro-posterior (Q) and ventral (R) views.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 122(6), Shimizu, T., Yabe, T., Muraoka, O., Yonemura, S., Aramaki, S., Hatta, K., Bae, Y.K., Nojima, H., and Hibi, M., E-cadherin is required for gastrulation cell movements in zebrafish, 747-763, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.