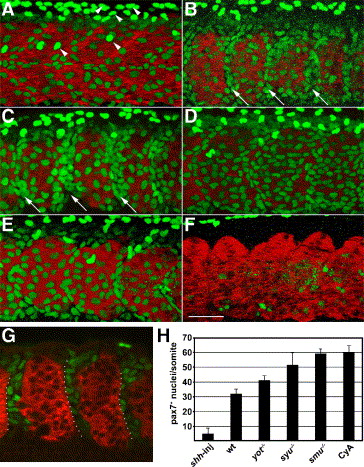
Fig. 2 Hedgehog signaling negatively regulates the number of Pax7+ myogenic precursors. Embryos were labeled at the prim5 (24 h) stage for Pax7 (green) and myosin (MF20, red). (A) In wild-type embryos, the surface of each somite has two types of Pax7+ myogenic precursors, moderately labeled cells that are part of the somite, and more brightly labeled, dorso-ventrally elongated neural crest cell nuclei. (B, C) smu(smo)-/- and CyA-treated wild-type embryos have more Pax7+ myogenic precursors than wild-type control embryos, particularly in the anterior part of each somite (arrows). (D, E) In syu(shh)-/- and yot(gli2)-/- embryos, the number of Pax7+ nuclei is intermediate between untreated wild-type and smu(smo)-/- or CyA-treated wild-type embryos. (F) shh mRNA-injected wild-type embryos have virtually no Pax7+ nuclei. (G) A single optical slice of a CyA-treated wild-type embryo through the middle part of somites, demonstrating the gaps between myotomes that are filled with Pax7+ cells. Many of the Pax7+ cells are within the anterior of each somite (dotted outline). (H) Quantitation of the number of Pax7+ myogenic precursors per somite in each genotype or treatment (mean of 5 embryos per genotype or treatment, somites 16–18 were counted; error bar = standard deviation). Panels A–F are projections of Z-stack confocal sections (see Materials and methods), panel G is a thin optical slice, all panels are anterior to the left, dorsal up; somite 17 is shown in each panel. Scale bar = 50 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 300(2), Feng, X., Adiarte, E.G., and Devoto, S.H., Hedgehog acts directly on the zebrafish dermomyotome to promote myogenic differentiation, 736-746, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.