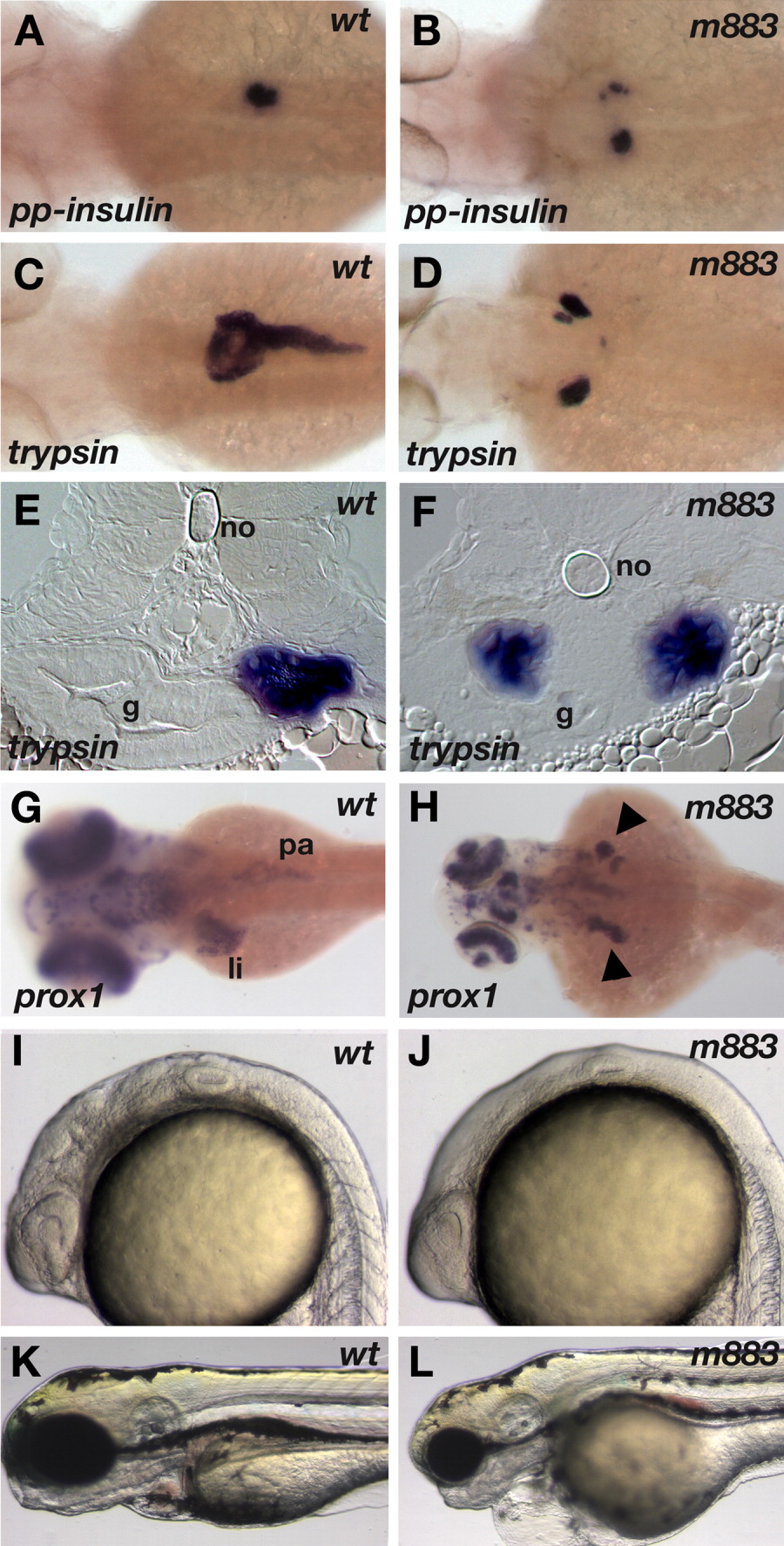
Fig. 1 The m883 mutation causes left-right isomerism of endodermal organs. Formation of endodermal organs in wild-type (A,C,E,G) and m883 mutant embryos (B,D,F,H). A,B: The mutation m883 was initially isolated based on the split appearance of the bilateral preproinsulin expression domain, here in a 3-dpf embryo. C,E: In wild type embryos, as judged from trypsin expression, the right-sided exocrine pancreas extends over several somites along the anterior-posterior axis. D,F: In mutant embryos, the exocrine pancreas is frequently found bilateral and appears shortened. G,H: Expression analysis of prox1 reveals the liver primordium, and demonstrates that liver tissue is also forming on both sides of m883 mutant embryos. I-L: Morphological phenotypes of m883 mutant embryos. Homozygous mutant embryos (J) can be clearly distinguished from wild-type (I) from the 22-somite stage on; the inflation of the brain ventricles fails to occur, while eyes and ears, notochord, and somites appear to develop largely normally. At day 4 (K, L), mutant embryos have severe heart defects, with no blood circulation, causing blood accumulation in the body and retarded growth. Dorsal views in A-D, G, H, with anterior to the left. Transversal sections in E, F, oriented dorsal at top. K,L: Lateral views, anterior to the left and dorsal up. g, gut; li, liver; no, notochord; pa, pancreas.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.