Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250708-26
- Publication
- Wang et al., 2025 - p21, ccng1, foxo3b, and fbxw7 contribute to p53-dependent cell cycle arrest
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
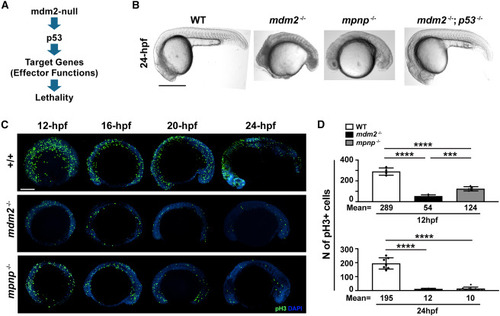
Loss of p21 partially rescues p53-dependent mdm2-null induced cell-cycle arrest (A) The conceptional diagram of mdm2-null induced embryonic lethality. Loss of mdm2 elevates p53 protein levels to induce downstream targets and effector functions to render the lethality. (B) Representative gross images of 24-hpf mdm2+/+, mdm2−/−; puma−/−; noxa−/−; p21−/− (mpnp−/−) and mdm2−/−; p53−/− embryos. Scale bar: 500μM. (C) pH3-stained mdm2+/+, mdm2−/−; mpnp−/− embryos at 12-, 16-, 20- and 24-hpf. Scale bar: 200μM. (D) Quantification of pH3 positive cells at 12 hpf (Top panel) and at 24 hpf (bottom panel). Each dot represents an individual. Bars represent mean ± SEM. ∗∗∗, p < 0.001.∗∗∗∗, p < 0.0001. Not statistical significance between mdm2−/− and mpnp−/− at 24 hpf. |