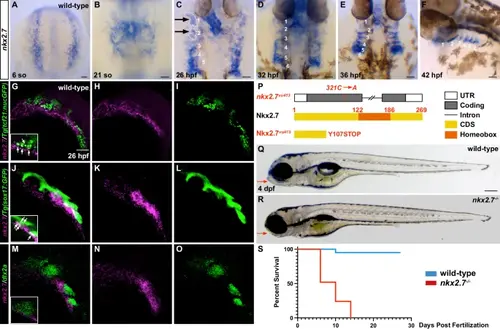
Fig. 2
|
Pharyngeal arch expression of nkx2.7 is necessary for jaw formation and larval survival.In situ hybridization (ISH) for nkx2.7 in wild-type embryos at 6 so (n = 5) (A), 21 so (n = 7) (B), 26 hpf (n = 5) (C), 32 hpf (n = 5) (D), 36 hpf (n = 20) (E), and 42 hpf (n = 20) (F) demarcates progressive expression in the lateral plate mesoderm, cardiac cone, pharyngeal arch (PA) primordia, cardiac tube, and mesendoderm of the PAs throughout early development. Numbers represent PA primordia 1-6. Black arrows and white dotted lines encircling PA1 and PA2 denote mesodermal cores (C). Dorsal views, anterior to the top (A–E) and lateral view, anterior to the left (F). Scale bar, 50 μm. Hybridization chain reaction (HCR) for nkx2.7 in Tg(tcf21:nucGFP) (n = 6) (G–I) and Tg(sox17:GFP) (n = 7) (J–L) wild-type embryos. nkx2.7 and dlx2a expression is reflected through HCR in wild-type embryos (n = 12) (M–O). Insets show single plane, higher magnification images of PA2. White arrows indicate double positive cells. Lateral views, anterior to the left. Scale bar, 50 μm. P Schematic depicts the zebrafish nkx2.7vu413 allele and the predicted wild-type and mutant Nkx2.7 protein products. The vu413 point mutation generated through TILLING is noted in red with the nucleotide transversion indicated above the gene and the corresponding codon change indicated next to the protein. The C- > A transversion at position 321 of the open reading frame leads to a nonsense mutation that is predicted to cause truncation of the protein prior to the homeodomain. Q, R Representative images of 4 dpf wild-type (n = 11) (Q) and nkx2.7−/− (n = 8) (R) embryos. Red arrows highlight normal jaw development in the wild-type embryo compared to a collapsed jaw in the nkx2.7−/− embryo. Lateral view, anterior to the left. Scale bar, 200 μm. S Kaplan-Meier survival curve depicts the pattern of larval death based on genotypic assessment in wild-type (n = 225) and nkx2.7−/− (n = 74) larvae. |