Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250401-17
- Publication
- Li et al., 2025 - Genetic inactivation of the β1 adrenergic receptor prevents cerebral cavernous malformations in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
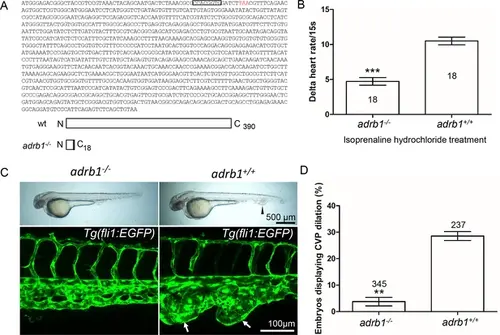
Adrb1 signaling is essential for CVP dilation. (A) The targeted adrb1 allele shows an 8-nucleotide deletion producing a pre-stop codon. Adrb1 null cDNA is predicted to encode truncated adrb1 protein. The wild type adrb1 protein contains 390 amino acids, while the predicted adrb1 null protein would contain 2 missense amino acids (gray bar) and would terminate after amino acid 18. (B) Isoprenaline hydrochloride (50µM) treatment at 72hpf lead to a heart rate increase in zebrafish, while the delta heart rate in adrb1-/- is significantly smaller than that of wild type. Heartbeat was counted in 18 embryos of each group before and immediately after adding the chemical. Paired two-tailed t test, p<0.0001. (C) After ccm2 CRISPR injection, representative bright field and confocal images of 2dpf Tg(fli1:EGFP) embryos show that wild type embryos display CVP dilation, while adrb1-/- embryos were resistant to this defect. Arrowhead and arrows indicate the dilation in CVP. Scale bar: 500 µm (bright field), 100 µm (confocal). (D) Paired two-tailed t test shows that percentage of embryos displaying CVP dilation is significantly smaller on adrb1-/- background than that of control embryos. p=0.0012. 345 adrb1-/- embryos and 237 control embryos from four experiments were examined for CVP cavernoma. |