Fig. 3 - Supplemental 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250327-55
- Publication
- Kondrychyn et al., 2025 - Combined forces of hydrostatic pressure and actin polymerization drive endothelial tip cell migration and sprouting angiogenesis
- Other Figures
-
- Fig. 1
- Fig. 1 - Supplemental 1
- Fig. 1 - Supplemental 2
- Fig. 1 - Supplemental 3
- Fig. 2
- Fig. 3
- Fig. 3 - Supplemental 1
- Fig. 3 - Supplemental 2
- Fig. 3 - Supplemental 3
- Fig. 3 - Supplemental 4
- Fig. 3 - Supplemental 5
- Fig. 3 - Supplemental 6
- Fig. 3 - Supplemental 7
- Fig. 4
- Fig. 4 - Supplemental 1
- Fig. 5
- Fig. 6
- Fig. 7
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
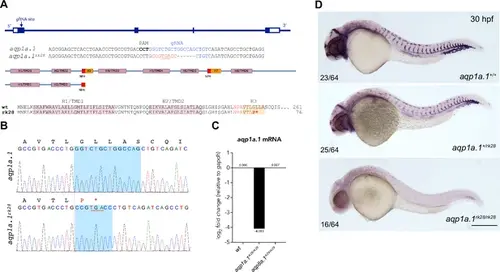
CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutation in zebrafish aqp8a.1 gene. (A) Zebrafish aqp8a.1 gene structure, gRNA binding site (in blue), aqp8a.1rk29 allele, Aqp8a.1 wildtype (261 aa), and Aqp8a.1rk29 (truncated at 73 aa) protein structure. The rk29 mutation causes a 4-nt deletion, which leads to a frameshift after Thr15 and premature termination codon at amino acid 73 after 58 missense amino acids, and as a result to the loss of six transmembrane domains/helices (H1/TMD1-H8/TMD6) and two membrane-inserted non-membrane-spanning helices (H3 and H7). (B) Sequence read showing 4-nt deletion (shadowed area in wildtype allele) in aqp8a.1rk29 allele (red dotted line). Amino acid sequence is shown above the nucleotide sequences. (C) qPCR analysis of aqp8a.1 mRNA expression in wildtype, aqp1a.1rk28/rk28 and aqp8a.1rk29/rk29 embryos. (D) Representative images of wildtype, heterozygote, and homozygote embryos after whole-mount in situ hybridization with aqp8a.1 RNA probe at 30 hpf. Scale bar, 250 µm. |