Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250131-40
- Publication
- Gence et al., 2024 - Gene expression patterns of the LDL receptor and its inhibitor Pcsk9 in the adult zebrafish brain suggest a possible role in neurogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
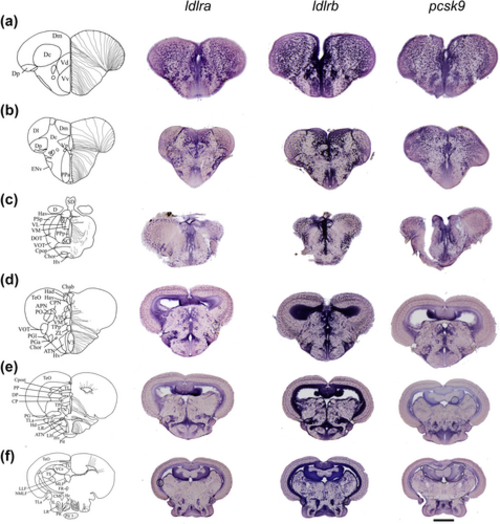
ldlra, ldlrb and pcsk9 in situ hybridization in the brain of adult zebrafish. (a–f) The schemes (left columns) provide the localization of the transversal brain sections with the name of the different brain nuclei and/or domains. (a–c) ldlra, ldlrb and pcsk9 in situ hybridization in the telencephalon (a,b), diencephalon with the anterior (b; PPa) and posterior (c; PPp) parts of the preoptic area. (d–f) ldlra, ldlrb and pcsk9 in situ hybridization in transversal brain section through the anterior part of the hypothalamus (D, Hv), the mediobasal hypothalamus (e; Hv LR) and the caudal hypothalamus (f; at the level of LR PR). Note that staining for each gene was detected in the anterior part of the hypothalamus, the periventricular nucleus of the posterior tuberculum (TPp), the central posterior thalamic nucleus (CP), the torus semi-circularis (TS) and midbrain parenchyma. The general overall pattern of expression for ldlra, ldlrb and pcsk9 was almost similar between the different genes and was almost ubiquitous within the brain. Bar: 400 μm (c–f), 100 μm (b) and 70 μm (a). |