Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230505-21
- Publication
- Wentworth et al., 2022 - Functional testing of BMP pathway variants identified on whole exome sequencing in a patient with delayed-onset fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) using ACVR1R206H -specific human cellular and zebrafish models
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
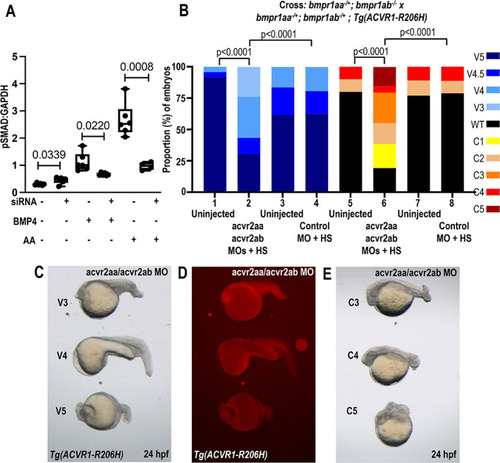
Co‐knockdown of BMPR1A and ACVR2A decreases BMP signaling in ACVR1 R206H HEK cells after stimulation with BMP4 or AA; knockdown of acvr2aa; acvr2ab; bmpr1aa; bmpr1ab partially rescues the ventralization phenotype in Tg(ACVR1‐R206Ha) zebrafish. (A) pSMAD 1/5/9 levels normalized to GAPDH loading control in ACVR1 R206H HEK 293T cells after transient transfection with siRNA targeting both BMPR1A and ACVR2A, and after stimulation with either BMP4, activin A (AA), or nonstimulated. N = 6 biological replicates for each condition except n = 4 for co‐transfected AA. Values of p are shown numerically with p < 0.05 denoting significance using unpaired, parametric t tests with Welch's correction. (B) acvr2aa; acvr2ab and bmpr1aa; bmpr1ab knockdown in Tg(ACVR1‐R206Ha) fish partially rescues the ventralization phenotype (Columns 1–4). Percent ventralized heat‐shocked (HS)‐Tg(ACVR1‐R206H) embryos in bmpr1aa; bmpr1ab mutant background after co‐injection with acvr2aa; acvr2ab or control MOs. Kruskal‐Wallis test was performed, statistical significance observed between columns 1 and 2 (p < 0.0001) and columns 2 and 4 (p < 0.0001) (Columns 1–4, n = 24, 46, 73, and 88, respectively). Genotyping was used to confirm that 6/10 V3 ventralized embryos were bmpr1aa −/− ; bmpr1ab −/− mutants as compared to 1/8 and 0/6 for more severe V4 and V5 ventralized embryos, respectively (see Fig. S7B). Percent dorsalized non‐Tg(ACVR1‐R206H) embryos in bmpr1aa; bmpr1ab mutant background after co‐injection of acvr2aa; acvr2ab or control morpholinos (MOs). Kruskal‐Wallis test was performed and statistical significance was observed between columns 5 and 6 (p < 0.0001) and columns 6 and 8 (p < 0.0001) (Columns 5–8, n = 49, 78, 57, and 71, respectively). (C,D) Ventralized (V3, V4, V5) HS‐Tg(ACVR1‐R206H) embryos in bmpr1aa; bmpr1ab mutant background following acvr2aa; acvr2ab MO co‐injection. (E) Dorsalized non‐Tg(ACVR1‐R206H) embryos in bmpr1aa; bmpr1ab mutant background following acvr2aa; acvr2b MO co‐injection. Parental genotypes are presented above each column in B. Control and acvr2aa; acvr2ab MOs were injected into separate clutches, and uninjected controls were scored from each clutch. Transgenic‐positive and transgenic‐negative embryos were sorted via mCherry fluorescence. MO = morpholino. |