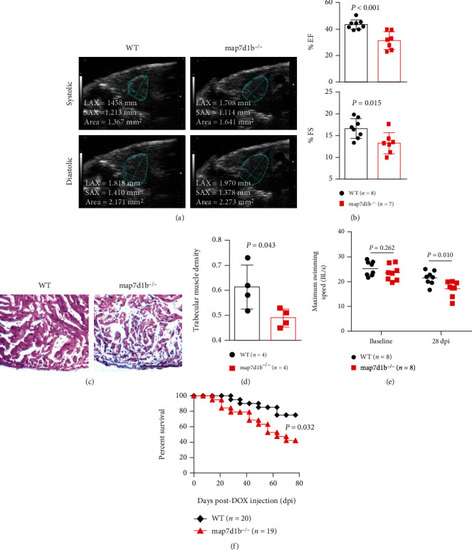
Disruption of map7d1b gene in the GBT239 homozygous mutant exacerbated doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction and heart failure. (a) Shown are examples of echocardiography images extracted from movies of beating hearts in WT controls and GBT239/map7d1b homozygous (map7d1b-/-) mutants at systole (upper panel) and diastole (lower panel) contraction. (b) Quantification of cardiac function indices of ejection fraction (EF) and fractional shortening (FS) measured by echocardiography in the map7d1b-/- mutant compared to WT control at 4 weeks postdoxorubicin injection. n=7-8, Student’s t-test. (c) Representative images of H&E staining of the ventricles at 4 weeks postdoxorubicin injection. Scale bar: 100 μm. (d) Quantification of trabecular muscle density in the map7d1b-/- mutant compared to WT controls at 4 weeks postdoxorubicin injection. n=4, Student’s t-test. (e) Maximum swimming speed of the map7d1b-/- mutant compared with the WT control at both baseline and 28 days postdoxorubicin injection (dpi). n=8, Student’s -test. (f) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of WT and map7d1b-/- mutant zebrafish injected with a single bolus of 20 μg/gram body mass (gbm). The map7d1b-/- mutant had a significantly reduced survival than WT controls. n=19–20, log rank test.
|

