Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210210-60
- Publication
- Quintanilla et al., 2020 - The Cdx transcription factors and retinoic acid play parallel roles in antero-posterior position of the pectoral fin field during gastrulation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
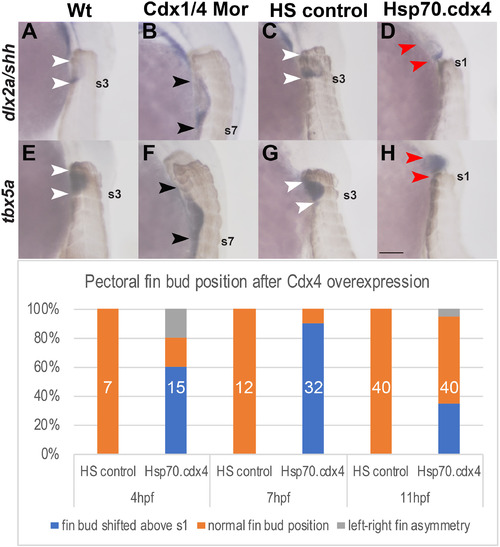
Cdx1a and Cdx4 regulate the position and size of the pectoral fin buds along the AP axis. (A–H) In situ hybridizations for the pectoral fin AER marker dlx2a (A–D), shh (A–D) and tbx5a (E–H) in lateral view at 36 hpf show caudal shift and expansion of the fin buds (B, F) as well as rostral shift of the pectoral fin bud (D, H) relative to the somites (brown). Fin buds are positioned at the level of somites 2–3 in wt (white arrowheads indicate somite level 2–3, A, E). Pectoral fin buds form at somite level 3–7 in Cdx-deficient embryos (black arrowheads in B, F indicate extent of fin buds that form adjacent to somites 3 and somite 7 (indicated as s7)). Pectoral fin buds form at somite levels 2–3 in HS controls (white arrowheads, C, G) while in Hsp70.cdx4 fish, they form rostral to the level of somite 1 (red arrowheads, D, H). (I) The frequency of rostral fin bud shifts after induced cdx4 overexpression beginning at either 4,7 or 11 hpf is indicated as % of total embryos. The corresponding numbers are: 9/15 embryos at 4 hpf, 29/32 embryos at 7 hpf and 14/40 embryos at 11 hpf. Total number of embryos used is indicated in white. Scale bar represents 100 μm. |
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 164, Quintanilla, C.A., Ho, R.K., The Cdx transcription factors and retinoic acid play parallel roles in antero-posterior position of the pectoral fin field during gastrulation, 103644, Copyright (2020) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.