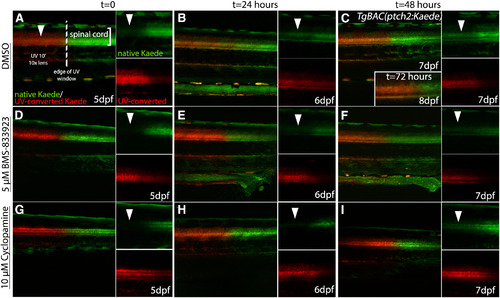
Figure 4.
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-201231-11
- Publication
- Male et al., 2020 - Hedgehog signaling regulates neurogenesis in the larval and adult zebrafish hypothalamus
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
Cya and BMS-833923 both block Hh signaling in zebrafish larvae. |