|
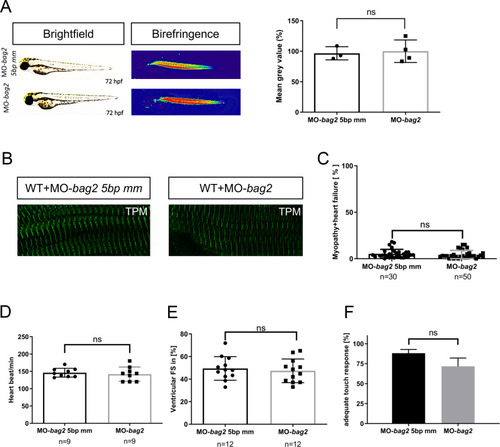
Targeted knockdown of <italic>bag2</italic> does not lead to heart and muscles dysfunction in zebrafish embryos.(A) Brightfield and birefringence images and the densitometric analysis of birefringence (n = 4) of MO-bag2 and MO-bag2 5bp mm injected embryos reveal that bag2 morphants do not develop a (cardio)-myopathy phenotype by 72 hpf. Representative samples are shown (P = 0.7891 determined using two tailed t-test). (B) Tropomyosin immunostainings of MO-bag2- and MO-bag2 5bp mm-injected embryos at 72 hpf demonstrate that bag2 morphants do not develop fiber disruptions. (C)bag2 morphants do not develop (cardio-)myopathy (only 4.50±4.43% of embryos exhibit a phenotype) (N = 3, n = 30/50, Mean± SD P = 0.5010 determined using two-tailed t-tests). (D) Heart rate quantification of bag2 morphants (146±12.64 heart beat/min), at 72 hpf does not show any impairment compared to bag2 5bp-mismatch morphants (142±20.57 heart beat/min) (N = 3, n = 9, mean ± S.D. P = 0.6490 determined using two-tailed t-tests). (E) FS of bag2 morphant ventricles at 72 hpf is not reduced (47.34±10.49%) compared to 5bp-mismatch-MO injected embryos (FS: 49.44±10.48%) (N = 3, n = 12, Mean± SD P = 0.6279 determined using two-tailed t-tests). (F) Touch evoked assay for bag2 morphants does not reveal a significant reduction in responsiveness to mechanical stimulus (71.67±4.22%) (N = 3, n = 50/25, mean ± S.D. P = 0.0941, determined using two-tailed t-tests).
|