Figure 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-201003-65
- Publication
- Wasel et al., 2020 - Chemical and Genetic Zebrafish Models to Define Mechanisms of and Treatments for Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
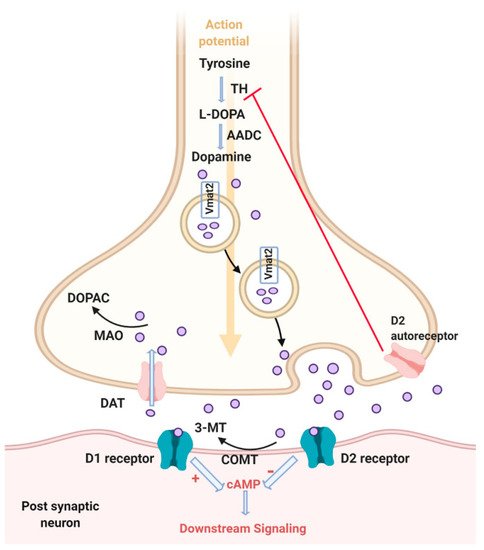
Dopamine signaling pathway. Tyrosine is converted to L-DOPA by the rate limiting step enzyme, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). Then dopamine is synthesized by action of the aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC). Dopamine is packed in the cytosol via vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (Vmat2). Dopamine is then released from vesicles into the synaptic cleft in response to an action potential. Dopamine can either bind to D1 receptor and activate adenylate cyclase and consequently activate downstream signaling through cAMP, or bind D2 receptor and inhibit adenylate cyclase and downstream signaling. Reuptake of dopamine from the synaptic cleft to the cytosol occurs through the dopamine transporter (DAT). Then dopamine can either be degraded to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) via monoamine oxidase (MAO) or repacked in vesicles via Vmat2. Dopamine can also be degraded in the synaptic cleft via catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) to 3 methyltyramine (3MT). Extracellular dopamine can bind to the D2 autoreceptor, which inhibits the synthesis of dopamine. Created with BioRender.com. |