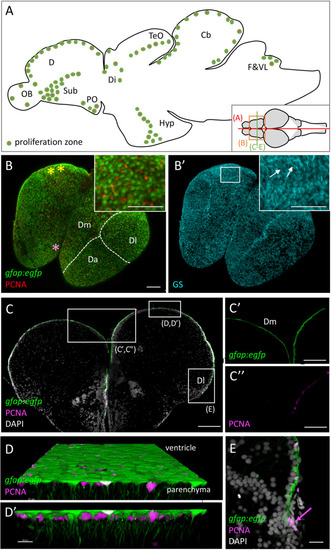
Progenitor cells in the zebrafish adult brain at 3 months-post-fertilization (mpf). (A) Scheme of a mid-sagittal section (anterior left) showing the localization of proliferation zones (colored dots) (Adolf et al., 2006; Grandel et al., 2006). (B,B’) Dorsal view of a whole-mount telencephalon from a gfap:egfp transgenic animal, processed in triple immunohistochemistry for GFP, PCNA (B), and GS (B’). Anterior is bottom left. Note the continuous layer of progenitor cells visible from the dorsal surface. Pallial territories are indicated by the dotted lines (see Dray et al., 2015). Yellow stars indicate the location of the territory homologous to the hippocampus (Ganz et al., 2015, and see Rodríguez et al., 2002 in goldfish), and the pink star the territory homologous to the amygdala (von Trotha et al., 2014). Anti-GS immunohistochemistry (B’) permits to see basal RG processes (arrows). (C–E) Cross-section of a telencephalon from a gfap:egfp transgenic animal, processed in double immunohistochemistry for GFP and PCNA and counter-stained with DAPI (C) and high magnifications of the domains boxed (C’,C”,E). In addition, a high magnification view of the ventricular zone of Dm is shown (D,D’) in 3D (Imaris software) to appreciate radial glial cell morphology. (E) Focus on NE progenitors at the pallial edge (arrow). Scale bars: (B,B’,C) 100 mm; (C’,C”) 30 mm; (D,D’) 20 mm; (E) 50 mm. Cb, cerebellum; D, dorsal part of the telencephalon (pallium) (Da: anterior part of D, Dm: medial part of D; Dl, lateral part of D); Di, diencephalon; F&VL, facial and vagal lobes; Hyp, hypothalamus; OB, olfactory bulb; PO, preoptic area; TeO, tectum opticum.
|

