Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-200709-38
- Publication
- Mitchell et al., 2020 - Targeted mutation of secretogranin-2 disrupts sexual behavior and reproduction in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
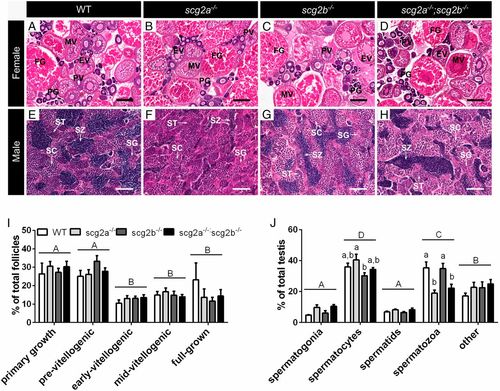
Histological assessments of ovaries (A–D and I) and testes (E–H and J) of WT, scg2a−/−, scg2b−/−, and scg2a−/−;scg2b−/− zebrafish at 4 mo of age. Ovarian follicular stages are labeled on top of their respective structure and abbreviated as follows: PG, primary growth follicle; PV, previtellogenic follicle; EV, early-vitellogenic follicle; MV, midvitellogenic follicle; FG, full-grown follicle. Spermatogonial cells in testes are indicated by arrows; SG, spermatogonia; SC, spermatocytes; ST, spermatids; SZ, spermatozoa. (Scale bars, 200 µm for females and 50 µm for males.) Gonads fixed in Bouin’s solution underwent standard histological procedures and 5- to 8-µm-thick sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin stain. Sections shown were selected to be representative of mean values shown in I (ovaries) and J (testes). (I) Percentages of primary growth, previtellogenic, early-vitellogenic, midvitellogenic, and full-grown oocytes in ovaries from females (mean + SEM, n = 5). (J) Percentage of area covered by spermatogonia, spermatocytes, spermatids, spermatozoa, and other tissues in testes from males (mean + SEM, n = 5). Uppercase letters (A, B, C, D) denote differences between gonad stages (P < 0.05), whereas lowercase letters (a, b, c, d) signify differences between genotypes within a stage (P < 0.05). Other details for histology are presented in SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods. |