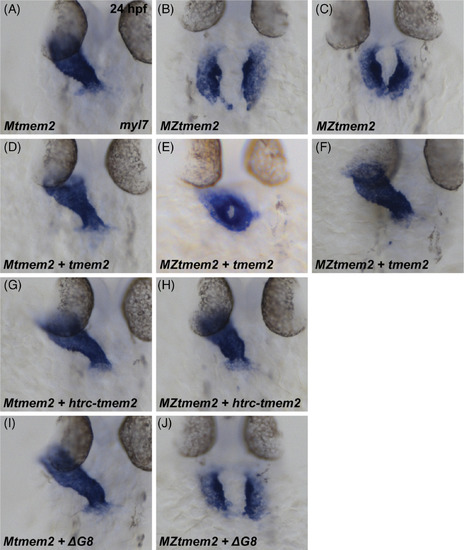
The ectodomain of Tmem2 is critical for promoting cardiac fusion. In situ hybridization indicates expression of myl7 in Mtmem2 (A, D, G, I) and MZtmem2 (B, C, E, F, H, J) mutant embryos at 24 hpf; dorsal views, anterior up. The heart tube assembles normally in Mtmem2 embryos (A), with no evident defects or delay in cardiac fusion, just as is observed in wild‐type and Ztmem2 mutant embryos.12 MZtmem2 mutant siblings, however, display either cardia bifida (B) or, less frequently, partial cardiac fusion (C). Expression of full‐length tmem2 in MZtmem2 mutants can facilitate cardiomyocyte movement to the midline (E) and frequently restores heart tube formation (F) (Table 2). Expression of htrc‐tmem2 in MZtmem2 mutants can also rescue the MZtmem2 cardiac fusion defects (H; Table 2). As with ΔC‐term and all other extracellular domain deletion variants, expression of the ΔG8 variant does not rescue cardiac fusion in MZtmem2 mutants (J; Table 2). Mtmem2 sibling embryos appear unaffected by expression of tmem2 (D) or tmem2 variants (G, I; Table 2)
|

