|
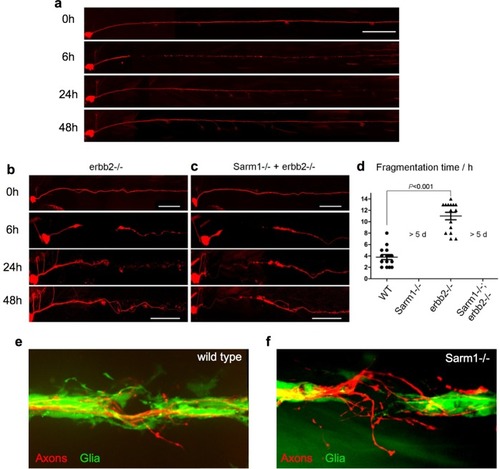
Schwann cells are not essential for the maintenance of Sarm1-deficient sensory axons.a–c Images of mCherry-expressing (red) transected axons in wild type (a), Erbb2−/− mutants (b), and Sarm1−/−; ErBb2−/− double mutants (c). Scale bar 100 μm. d Quantification of transected axon fragmentation in Erbb2−/− and Sarm1−/−; ErBb2−/−. Error bar = SEM, p value from one-way ANOVA test, n = 15 (each group). e Image of from Supplementary Movie 1, showing the discrete local defasciculation of regenerated the sensory fiber (red) and the bridging of the glial gap by Schwann cells (green) in a wild-type specimen. f Equivalent experiment, taken from Supplementary Movie 2, showing a more pronounced local defasciculation of the regenerated the sensory fiber (red) in a Sarm1-mutant specimen. Note that the bridging of the glial gap does not occur.
|