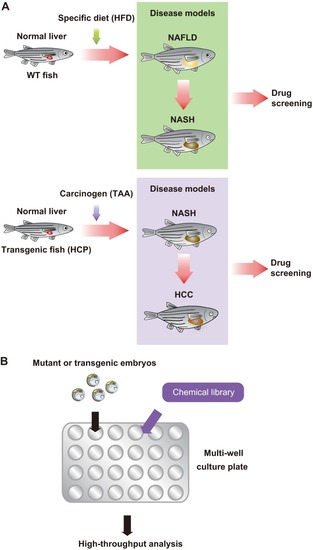
Drug screening strategy using fish disease models. (A) An overview of the NAFLD, NASH and HCC drug screening strategy in fish models. WT or transgenic (HCP) fish are raised on a specific diet (HFD) or treated with a specific carcinogen (TAA), giving rise to NAFLD and NASH, or NASH and HCC, respectively. The disease models are exposed to candidate drugs to determine whether the development of NAFLD, NASH or HCC can be mitigated. (B) Small-molecule inhibitor screen. Chemical libraries can be aliquoted to multi-well plates that contain fish growth medium. Large numbers of mutant or transgenic fish can be mated to generate thousands of embryos, which are placed in the multi-well plates containing medium and test reagents. These multi-well plates easily allow the detailed observation of embryo morphology under a dissecting microscope. To investigate chemical-induced changes in specific markers, several techniques have been established to perform high-throughput analysis, such as whole-mount immunohistochemistry or whole-mount in situ hybridization on large numbers of embryos.
|