Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-190604-11
- Publication
- Kopton et al., 2018 - Cardiac Electrophysiological Effects of Light-Activated Chloride Channels
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
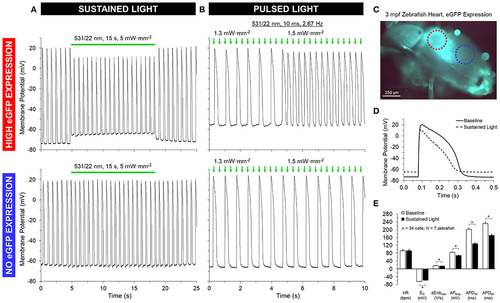
GtACR1 activation depolarizes ventricular myocyte membrane potential in isolated zebrafish hearts. Regions of high or no eGFP expression on the ventricle of 3-months post fertilization (mpf) zebrafish isolated hearts were illuminated by a 0.16 mm2 spot of 531/22 nm light sustained for 15 s or pulsed for 10 ms at a rate 2–3 × sinus heart rate. (A,D–E) In the case of sustained light, in regions displaying eGFP expression (red circle in C) there was an immediate increase in resting membrane potential (ER) and a decrease in the maximum rate of membrane depolarization (dE/dtmax), AP amplitude (APAmp), and APD at 50% and 90% repolarization (APD50 and APD90). (B) In the case of pulsed light, the heart could be stimulated when light intensity was increased to supra-threshold values. (A,B) In both cases, there was no effect seen in regions displaying no eGFP expression (blue circle in C). *indicates p < 0.0001 by two-tailed paired Student's t-test. |