Fig. 7
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180720-14
- Publication
- Burns et al., 2018 - Variants in EXOSC9 Disrupt the RNA Exosome and Result in Cerebellar Atrophy with Spinal Motor Neuronopathy
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
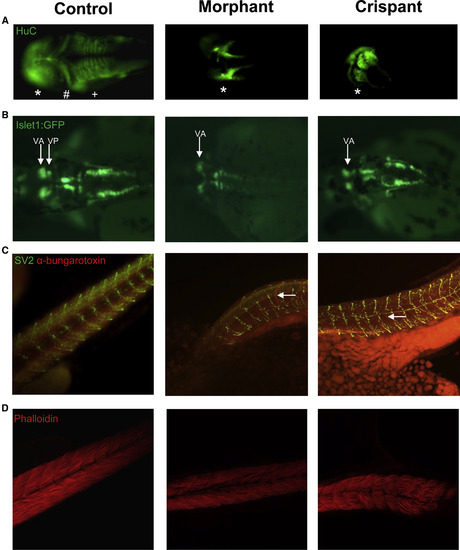
Knockdown of exosc9 in Zebrafish Causes Abnormal Neuromuscular Development (A) Whole-mount immunofluorescence of the pan-neuronal marker HuC shows that the midbrain (∗) appears abnormal and the cerebellum (#) and hindbrain (+) are absent in representative exosc9 morphants and crispants compared with uninjected controls. (B) Islet1:GFP transgenic morphant and crispant zebrafish have absent cranial posterior nerve V (Vp). (C) Whole-mount immunofluorescence of synaptic vesicle 2 (SV2, motorneurons, green) and α-bungarotoxin (neuromuscular junctions, red) shows that motoneurons and neuromuscular junctions failed to properly develop in exosc9 morphants and crispants compared with uninjected controls (white arrows). (D) Phalloidin staining shows that muscle failed to develop properly. Fibers were sparser, more spread out, and irregular in the exosc9 morphants and crispants. All experiments were performed in 48 hpf zebrafish. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |