Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180705-5
- Publication
- Viljoen et al., 2018 - A Simple and Rapid Gene Disruption Strategy in Mycobacterium abscessus: On the Design and Application of Glycopeptidolipid Mutants.
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
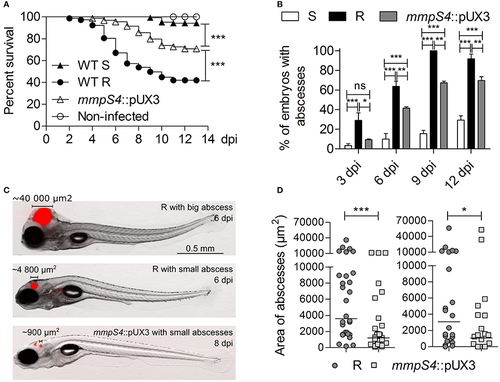
Low-level GPL producing mmpS4::pUX3 is more virulent than the S variant in zebrafish embryos, but not as virulent as the R variant. (A) Survival curves of zebrafish embryos infected with different strains. Killing of zebrafish embryos over the course of the experiment by different mycobacterial strains were compared using the Mantel-Cox log rank test. Shown is the pooled data from five independent experiments. In each experiment, 25–30 embryos were injected each with 200 ± 50 cfu. (B) Kinetic of abscess appearance in the population of infected embryos over a 12-day infection period showing retarded abscess appearance in mmpS4::pUX3-infected embryos compared to embryos infected with the R variant. Histograms and error bars represent means and their associated standard errors calculated from two independent experiments using 20 embryos per bacterial strain on each occasion. Data was analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-tests. Ns, non-significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (C) Representative images of embryos infected with the R variant at 6 dpi and mmpS4::pUX3 at 8 dpi showing smaller abscesses in the case of mmpS4::pUX3. (D) Scatterplots from two independent experiments showing sizes in area of the largest abscess per infected embryo over the 12-days infection period (n = 20 per bacterial strain in each experiment). Median abscess area between the R variant and mmpS4::pUX3 were statistically compared using a one-tailed Mann Whitney test. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Days 7-13 |