Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180529-26
- Publication
- Zhou et al., 2018 - Generation of all-male-like sterile zebrafish by eliminating primordial germ cells at early development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
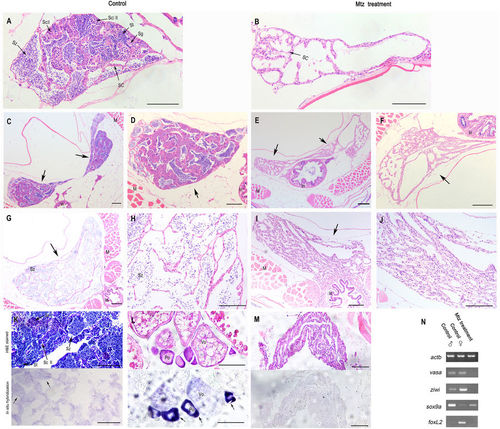
Histological analysis revealed the absence of germ cells at various developmental phases in the testis of MTZ-treated adult zebrafish. Transverse sections showing that the gonads of control zebrafish (A,C,D,G,H) and the ones of MTZ-treated zebrafish (B,E,F,I,J) at 100-dpf. At top of bilateral testis in the control adult zebrafish, germ cells with various developmental phases were found: spermatogonia, primary spermatocytes ScI, secondary speratocytes ScII, spermatids and spermatozoa (A), whereas MTZ-treated zebrafishes were found to have only Sertoli cells which were derived from somatic cells (B). Testis (arrow) near the bilateral gonadal junction also carried numerous seminiferous tubules with irregular shape in control adult fish (C,D), but there was no germ cells in the gonad (arrow) of the MTZ-treated fish at any developmental phases observed (E,F, arrow). Seminal vesicle-like structures were found in cross-section of the testis adjacent to the gonopore. The organ (arrow) consisted of numerous cavities communicated with each other, that contained a large quantity of sperm cells in the control zebrafish (G,H). No sperm was detected within the seminal vesicle in gonads (arrow) of the MTZ-treated zebrafish, so the cells of cavities which derived from somatic cells formed net structures (I,J). Transverse sections showing that the gonads of control male zebrafish at 100-dpf (K, upper panel) carried normal testis (black arrow) with germ cells at different developmental phases and had weak vasa expression in gonads (K, lower panel, black arrow) detected by in situ hybridization, the gonads of control female zebrafish at 100-dpf (L, upper panel) carried normal ovary and had strong vasa expression in developing oocytes (L, lower panel, black arrow) detected by in situ hybridization, whereas the gonads of MTZ-treated zebrafish at 100-dpf had only somatic gonadal cells (M, upper panel) and had no vasa expression (F, lower panel) detected by in situ hybridization. (N) RT-PCR results showing the expressions of vasa and ziwi were detected in the gonads of control male and female zebrafish, but not in the zebrafish developed from the MTZ-treated embryos, and strong expressions of sox9a and foxl2 were detetced in control male zebrafish and control female zebrafish respectively, weak expression of sox9a was found in control female zebrafish and MTZ-treated zebrafish, and no expression of foxl2 was detetced in control male zebrafish and MTZ-treated zebrafish. Expression of actb was used as positive control. Sg: spermatogonia, Sc I: Primary spermatocytes, Sc II: Secondary spermatocytes, St: Spermatids, Sz: Spermatozoa, SC: Sertoli cell, In: Intestine, M: Muscle, K: Kidney, Po: Primary oocyte, Vo: Vitellogenic oocyte. Scale bars = 20 µm. |