FIGURE
Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-180411-16
- Publication
- Winata et al., 2017 - Cytoplasmic polyadenylation-mediated translational control of maternal mRNAs directs maternal to zygotic transition
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. 4
|
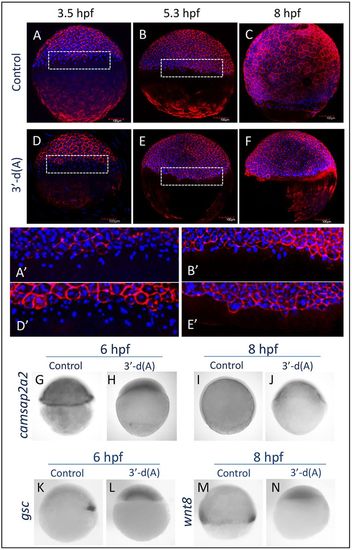
Phenotype caused by CPA inhibition. (A-C) At 3.5 and 5.3 hpf, the external yolk syncytial layer (e-YSL) could be observed in control embryos. (D-F) Embryos treated with 3′-dA beginning at the one-cell stage to 3.5 hpf still had visible e-YSL at 3.5 hpf, but this structure disappeared by 5.3 hpf, and epiboly did not proceed further (n=5). (G-J) Whole-mount in situ hybridization with the YSL marker camsap2a2 confirmed the absence of e-YSL up to 8 hpf (n=8). Other gastrulation markers, including dorsal shield (K-L; n=8) and mesendodermal cells expressing wnt8 (M,N; n=8), were also absent. |
Expression Data
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Condition: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Shield to 75%-epiboly |
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | High to 75%-epiboly |
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development