Fig. S2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-161212-3
- Publication
- Randlett et al., 2013 - Cellular requirements for building a retinal neuropil
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
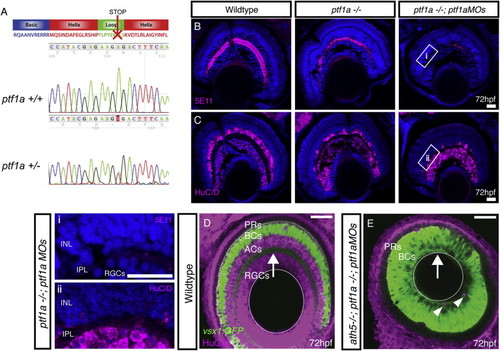
Elimination of ACs through Ptf1a Disruption, Related to Figure 2 (A) The ptf1asa126 mutation is an A to T conversion, which results in a non-sense mutation at amino acid 126 of 265. This results in a truncation within the loop of the basic helix-loop-helix DNA binding domain. (B and C) Immunostaining of retinal cryosections using (B) 5E11 to stain AC neurites and (C) anti-HuC/D to stain RGC and AC cell bodies, indicates that some ACs remain in homozygous ptf1a−/− mutants. Injection of ptf1a morpholinos into ptf1a−/− mutants, causes a further reduction in ACs numbers, where large stretches of retina lack 5E11 staining and HuC/D positive cells in the AC layer (higher magnification inserts given in: i, and ii). (D) WT retina with the vsx1GFP labeling BC axons in the IPL (arrow) and ACs/RGCs labeled with HuC/D. (E) In the ath5−/−;ptf1a−/−; ptf1aMO, AC/RGC-free retina, the IPL is positioned along the basal surface of the retina (arrow). Few remaining ACs shown with arrowheads. |