FIGURE
Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160226-21
- Publication
- Wu et al., 2016 - Spatially Resolved Genome-wide Transcriptional Profiling Identifies BMP Signaling as Essential Regulator of Zebrafish Cardiomyocyte Regeneration
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. 2
|
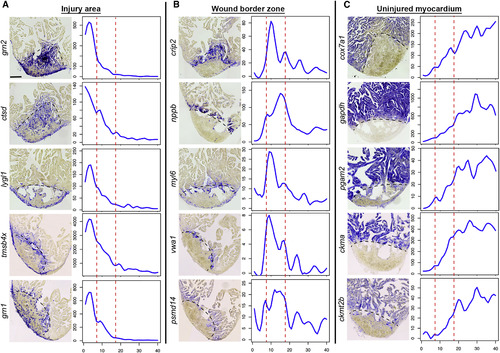
In Situ Hybridization Validates Tomo-Seq Results In situ hybridization for genes identified by tomo-seq to be enriched in the injury area (zone I) (A), wound border zone (zone II) (B), or the uninjured myocardium (zone III) (C) at 3 dpi (n = 3). Left: representative in situ staining; right: expression traces from tomo-seq data. y axis, read counts; x axis, section number. Scale bar, 100 µm. Dashed black line indicates wound boundary on sections. Red lines in plots surround the border zone. |
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 36(1), Wu, C.C., Kruse, F., Vasudevarao, M.D., Junker, J.P., Zebrowski, D.C., Fischer, K., Noël, E.S., Grün, D., Berezikov, E., Engel, F.B., van Oudenaarden, A., Weidinger, G., Bakkers, J., Spatially Resolved Genome-wide Transcriptional Profiling Identifies BMP Signaling as Essential Regulator of Zebrafish Cardiomyocyte Regeneration, 36-49, Copyright (2016) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell