Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150824-16
- Publication
- Helker et al., 2015 - The hormonal peptide Elabela guides angioblasts to the midline during vasculogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
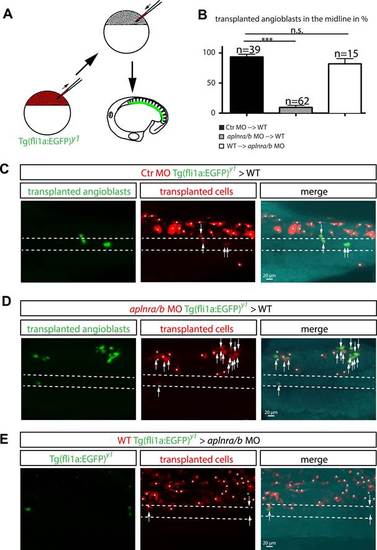
Cell autonomous requirement for Apelin receptor signaling in angioblasts. (A) Experimental design: mini-ruby injected cells from ctr MO (C) aplnra/b MO (D) or WT (E) Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 embryos were transplanted into WT or aplnra/b MO host embryos and scored for their migration to the midline. (B) Quantification: 93.6% of ctr MO injected (n = 39 GFP + angioblasts, 7 embryos), but only 9.4% of aplnra/b deficient (aplnra/b MO injected; n = 62 GFP+ angioblasts, 5 embryos) donor angioblasts migrated to the midline in WT host embryos. In contrast, 81.9% of WT donor angioblasts (n = 15 GFP+ angioblasts, 6 embryos) migrated to the midline in aplnra/b deficient host embryos. Error bars represent SEM, calculated using the standard deviation of percent of angioblasts in the midline per embryo. Statistical analysis showed significance using 2 way ANOVA and t-test, with p *** = 3.44577E-08 for aplnra/b MO in WT, and p = 0.232995135 (not significant, n.s.) for WT in aplnra/b MO. see also Figure 5—source data 1. (C–E) Confocal projections showing representative embryos of the transplantation experiments at 17 hpf. Arrows indicate transplanted angioblasts; asterisks label transplanted cells, which are not angioblasts; dashed lines indicate the midline. |