Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140612-9
- Publication
- Ogawa et al., 2014 - Habenular kisspeptin modulates fear in the zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
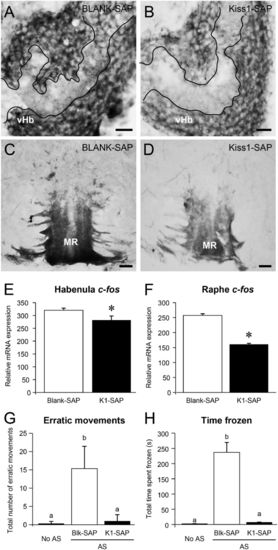
Effect of Kiss1-SAP on Kiss1 immunoreactivity, on c-fos mRNA expression levels in the habenula and the median raphe, and on AS-evoked fear response. (A–D) Transverse sections of Kiss1 immunoreactivity in the ventral habenula (vHb; A and B) and the median raphe (MR; C and D) in the brain of zebrafish injected with Blank-SAP (A and C) or Kiss1-SAP (B and D) at 12 d after injection (103 mol per fish; intracranial administration, n = 3 per group). Kiss1 immunoreactive fibers were relatively reduced in the area of neuropil of the vHb (encircled by white lines) in Kiss1-SAP-treated fish compared with the Blank-SAP group (A and B). Kiss1 immunoreactive axons entering the MR were relatively weak, and fewer fibers were seen in the superior raphe regions in Kiss1-SAP-treated fish compared with in the Blank-SAP group (C and D). (Scale bars, 20 µm.) (E and F) Graphs showing the effect of Kiss-SAP on mRNA levels of c-fos in the habenula (E) and raphe (F) regions at 3 d after injection (n = 10 per group). (G and H) Graphs of behavioral parameters of fear response: the number of erratic movements (G) and the freezing time (H) in the zebrafish injected with Blank-SAP (open column) or Kiss1-SAP (closed column) (105 mol per fish; intracranial administration, n =10 per group) at 3 d after injection. Behavior data of control (no AS, fish treated with distilled water) are provided for comparison. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Significant differences (P < 0.05) between groups are indicated by different letter codes; one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey’s test. |