Fig. 11
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-131213-3
- Publication
- Sun et al., 2013 - Imaging-based chemical screening reveals activity-dependent neural differentiation of pluripotent stem cells
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
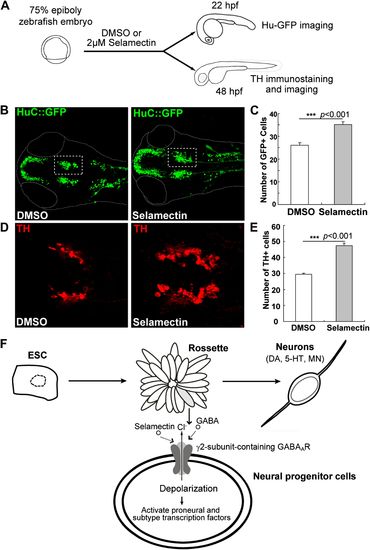
Selamectin promotes neurogenesis in vivo in the developing zebrafish brain.(A) Scheme of the selamectin treatment on HuC:GFP transgenic zebrafish embryos. (B) Representative images show that selamectin (2 μM, 14 hr from 8 hpf to 22 hpf) increases Huc-GFP signal. (C) Quantification of the midbrain cluster (boxed) shows a significant difference between two groups (t-test, n = 20, p<0.001). (D) Representative images show increased DA neurons in selamectin-treated embryos (2 μM for 40 hr from 8 hpf to 48 hpf). (E) Quantification of the ventral forebrain DA neurons shows a significant difference between two groups (t-test, n = 10, p<0.001). (F) A schematic model shows the effect of selamectin on neuronal differentiation from mESCs. |