FIGURE
Fig. 1
Fig. 1
|
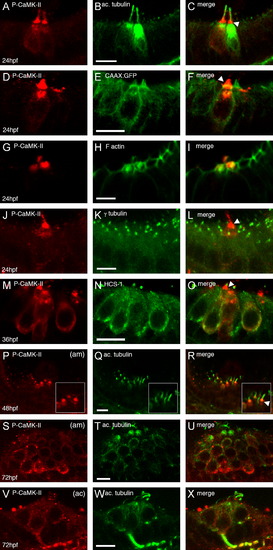
Localization of activated CaMK-II in 24–72 hpf zebrafish embryonic ears. Embryos were immunostained for P-CaMK-II (A, D, G, J, M, P, S, V) in wild-type or CAAX:GFP embryos and then counterstained for acetylated tubulin (B, Q, T, W), F actin (H), γ tubulin (K) or HCS-1 (N). Arrowheads point to the most intense P-CaMK-II staining. Images were acquired laterally with anterior to the left at 24 hpf (A–L), 36 hpf (M–O), 48hpf (P–R) or 72 hpf (S–X). am=anterior macula, ac=anterior crista. All scale bars=5 μm. |
Expression Data
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Antibodies: | |
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-5 to Protruding-mouth |
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 381(1), Rothschild, S.C., Lahvic, J., Francescatto, L., McLeod, J.J., Burgess, S.M., and Tombes, R.M., CaMK-II activation is essential for zebrafish inner ear development and acts through Delta-Notch signaling, 179-88, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.