Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130218-22
- Publication
- Tokarz et al., 2013 - Zebrafish 20beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 is important for glucocorticoid catabolism in stress response
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
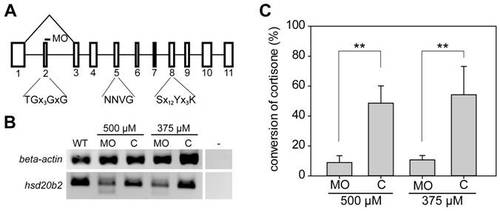
Analyses of knock down efficiency of an hsd20b2 splicing morpholino reveal reduction of enzymatic activity. (A) In the genomic structure of zebrafish hsd20b2, exons are indicated by boxes and numbered. Below, the important short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase motifs (single letter amino acid code) are denoted. ‘x’ denotes any amino acid residue, and when present, the subsequent number indicates the number of × residues. The splice site targeted by the morpholino is indicated by a dash. Morpholino-induced mis-splicing is illustrated by the triangle above the genomic structure. Exons are to scale, whereas the space between the exons does not reflect the respective intron size. (B) The analyses of morpholino efficiency at the mRNA level by RT-PCR using primers that prime within the first and fourth exons demonstrate mis-splicing in morpholino-injected fish (MO). The smaller PCR product is absent from samples of the control morpholino-injected fish embryos (C). The respective morpholino concentration used is denoted. β-actin controls were included for normalization. (C) The knock down efficiency was analyzed by assaying the enzymatic activity that converts cortisone to 20β-hydroxycortisone in morpholino (MO)- and control morpholino (C)-injected fish. The respective morpholino concentration used is denoted and mean values with standard deviations from four biological replicates are presented. Significant levels are indicated: ** p<0.01. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | Long-pec to Protruding-mouth |